Health, Fitness,Dite plan, health tips,athletic club,crunch fitness,fitness studio,lose weight,fitness world,mens health,aerobic,personal trainer,lifetime fitness,nutrition,workout,fitness first,weight loss,how to lose weight,exercise,24 hour fitness,
Labels
Technology
New Post
Set your posture straight with this easy at-home pilates workout
from Fitness | body+soul https://ift.tt/2FND3i4
People can make better choices when it benefits others
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/3aQEMyI
Posture Hero with Peaches Pilates
from Fitness | body+soul https://ift.tt/34tlP3M
Optical illusions explained in a fly's eyes
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/34wsBGe
In one cancer therapy, two halves are safer than a whole
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/3go8FHH
Ventilators could be adapted to help two COVID-19 patients at once
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/3lh4IIE
Machines rival expert analysis of stored red blood cell quality
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/3jaEFkl
This healthy butter chicken is the ultimate takeaway dupe
from Nutrition | body+soul https://ift.tt/32Bqtuj
‘Pilates is my religion and these are the only tights I wear’
from Fitness | body+soul https://ift.tt/3aSvDWk
New surgical approach for women at risk of ovarian cancer
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/3jbbA8E
Wide variations in car seat breathing assessment conducted on premature newborns
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/2Yt0ROX
Finding a way to STING tumor growth
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/2YsHzci
Mechanisms identified to restore myelin sheaths after injury or in multiple sclerosis
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/2YwrL8r
When it comes to supporting candidates, ideology trumps race and gender
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/3lfDW3m
Mother transmitted COVID-19 to baby during pregnancy, physicians report
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/2Qj0Rwb
Autistic people's nerve cells differ before birth
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/2YxRj5g
Blood pressure medication improves COVID-19 survival rates, research finds
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/31p6WOf
New surgical approach for women at risk of ovarian cancer
from Women's Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/3jbbA8E
5 ways to ease pain using the mind-body connection
I smashed my elbow a few weeks ago. There was no bone break — just a bad bruise after slipping in the kitchen and landing on my arm — but at times the pain has been excruciating. So I’ve been following doctor’s orders: babying my elbow, icing it, and taking an occasional over-the-counter painkiller. (PS: I wear sneakers in the kitchen now.)
Something else has helped, too: mind-body therapies. These approaches aim to change our awareness of pain and retrain the way we respond to it. The therapies can help us control pain — such as long-lasting back pain — or live with it better. While these techniques won’t erase pain, they can help change perception of pain intensity through distraction, relaxation, and reframing our thoughts.
Five mind-body therapies to consider for pain relief
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). This talk therapy teaches people to redirect their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in response to chronic pain. For example, when a pain flare-up strikes, instead of bracing yourself and thinking, “Oh no, here it comes again,” tell yourself you’ve handled this before, and focus instead on your favorite place in the world: picture it in your mind, and feel how happy or relaxed you are when you’re there. A therapist trained in CBT can train you to hone your skills.
Deep breathing. We typically take short little breaths without noticing our breathing, especially when we’re in pain. Focusing on breathing and taking deep breaths quiets the mind and induces the relaxation response, a well-studied physiologic response that counteracts the stress response, and may lessen chronic pain severity. To practice deep breathing:
- Breathe in slowly through your nose, allowing your chest and lower belly to rise as you fill your lungs completely.
- Now exhale slowly through your mouth or nose.
- Practice deep breathing for several minutes.
Meditation. Like deep breathing, meditating triggers the relaxation response and may reduce the perception of pain. You can use many methods to meditate, such as transcendental meditation (repeating a word, phrase, or sound to quiet your thoughts); yoga (a series of strengthening and stretching postures combined with breathing techniques); or mindfulness meditation (focusing objectively on negative thoughts as they move through your mind, so you can achieve a state of calm).
One simple way to meditate:
- Sit quietly, close your eyes, and focus on your breathing.
- Say a word such as “peace” or “one” each time you exhale.
- Don’t worry about thoughts that come to mind; you can come back to them later. Continue to repeat your word and focus on breathing.
Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR). This approach combines mindfulness meditation and yoga to build awareness and acceptance of moment-to-moment experiences, including pain. A 2019 study published in the journal Evidence-Based Mental Health found MBSR was just as effective as CBT at reducing pain and depression, and improving physical functioning, compared with usual care or no care. You’ll find MBSR programs at hospitals, universities, and meditation centers, and online videos.
Relaxation. Relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation, may also help reduce the perception of pain. To try progressive muscle relaxation, start with your facial muscles and work your way down the body. Tighten each muscle or muscle group for 20 seconds before slowly releasing the contraction. As the muscle relaxes, concentrate on the release of tension and the sensation of relaxation.
The post 5 ways to ease pain using the mind-body connection appeared first on Harvard Health Blog.
from Harvard Health Blog https://ift.tt/2CYjxyu
Antibodies that may protect against COVID-19
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/2FKGK8a
Failure to 'flatten the curve' may kill more people than we thought
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/3j2aNqq
None of the most common blood pressure medications increased the risk of depression, some lowered the risk
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/3aQvjY6
Deep chest compressions can prevent brain damage during cardiac arrest
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/34FOl2z
None of the most common blood pressure medications increased the risk of depression, some lowered the risk
from Women's Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/3aQvjY6
Yoga linked with improved symptoms in heart patients
from Top Health News -- ScienceDaily https://ift.tt/3aQm8qw
Weekly Health Quiz: Mercury and COVID-19
1 Which of the following organizations conducted a highly successful campaign promoting trans fat in the 1980s, resulting in an epidemic of heart disease?
- Center for Science in the Public Interest
In the 1980s, CSPI conducted a highly successful campaign promoting trans fat, resulting in an epidemic of heart disease. It later white-washed its history, omitting its promotion of trans fat from the organization's historical timeline. Learn more.
- American Public Health Association
- National Institutes of Health
- Society for Public Health Education
2 Which former FDA commissioner now sits on the board of directors at Pfizer, which was granted a $1.95 billion deal with the U.S. government to provide Americans with 100 million doses of its COVID-19 vaccine?
- Margaret Hamburg
- Scott Gottlieb
Dr. Scott Gottlieb, who served as commissioner of the FDA from May 2017 to April 2019, was elected to Pfizer's board of directors at the end of June 2019. Learn more.
- Stephen Ostroff
- Robert Califf
3 According to mounting scientific evidence, SARS-CoV-2, responsible for COVID-19 disease, spreads via contact with contaminated surfaces (fomites):
- Poorly
According to mounting scientific evidence, SARS-CoV-2 spreads poorly via contact with contaminated surfaces. Scientists warn that making deep-cleaning a priority is not going to have a significant impact on the spread of SARS-CoV-2, as surface transmission appears to be minimal in the first place. Learn more.
- Moderately
- Effectively
- Not at all
4 A "COVID-19 case" refers to:
- A positive PCR test
- A positive antibody test
- A clinical diagnosis of someone who exhibits severe respiratory illness characterized by fever, coughing and shortness of breath
"COVID-19" refers to a clinical diagnosis of someone who exhibits severe respiratory illness characterized by fever, coughing and shortness of breath. If you test positive but are asymptomatic, you do not "have COVID-19" and should not be counted as a "COVID-19 case." Learn more.
- Someone who died with or from SARS-CoV-2 infection
5 Which of the following foundations is presently the largest funder of the World Health Organization if the U.S. holds good on withdrawing its WHO funding?
- Jarl Hjalmarson Foundation
- Clinton Foundation
- Paul and Nancy Pelosi Charitable Foundation
- Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation is the top donor to the WHO, as the U.S. has withdrawn its funding. Learn more.
6 According to an analysis by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Agency for Healthcare Research Quality of health data collected from 376,452 individuals who received a total of 1.4 million doses of 45 vaccines, vaccine injuries occur in:
- 1 in 1 million people
- 10 in 1 million people
- 1 in 40 people
According to an analysis by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Agency for Healthcare Research Quality, 1 in 40 people are injured by vaccines. Learn more.
- 1 in 2 people
7 Which of the following is a significant source of environmental mercury pollution?
- Dentists
Dental amalgam is a significant source of environmental mercury pollution. Learn more.
- Bicycle manufacturers
- Surgeons
- Logging industry
from Articles https://ift.tt/3gvgNq8
via IFTTT
Quercetin and Vitamin C: Synergistic Therapy for COVID-19
Quercetin was initially found to provide broad-spectrum protection against SARS coronavirus in the aftermath of the SARS epidemic that broke out across 26 countries in 2003.1,2,3 Now, some doctors are advocating its use against SARS-CoV-2, in combination with vitamin C, noting that the two have synergistic effects.
Incidentally, ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and the bioflavonoid quercetin (originally labeled vitamin P) were both discovered by the same scientist — Nobel prize winner Albert Szent-Györgyi.4,5 Quercetin’s antiviral capacity has been attributed to five main mechanisms of action:
- Inhibiting the virus’ ability to infect cells by transporting zinc across cellular membranes
- Inhibiting replication of already infected cells
- Reducing infected cells’ resistance to treatment with antiviral medication
- Inhibiting platelet aggregation — and many COVID-19 patients suffer abnormal blood clotting
- Promoting SIRT2, thereby inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome assembly involved with COVID-19 infection
Similarly, vitamin C at extremely high doses also acts as an antiviral drug, effectively inactivating viruses. During the 2003 SARS pandemic, a Finnish researcher called6 for an investigation into the use of vitamin C after research showed it not only protected broiler chicks against avian coronavirus, but also cut the duration and severity of common cold in humans and significantly lowered susceptibility to pneumonia.
The MATH+ Protocol
While high-dose vitamin C is new for COVID-19 treatment, it’s been used as a treatment for sepsis since about 2017. The vitamin C-based sepsis treatment was developed by Dr. Paul Marik, a critical care doctor at Sentara Norfolk General Hospital in East Virginia, which has since adopted it as standard of care for sepsis.
In the interview above, Marik explains how the COVID-19 critical care protocol grew out of his sepsis treatment, as he and other doctors noticed there were many similarities between sepsis and severe COVID-19 infection, in particular the out-of-control inflammatory cascade.
To address the differences between the two conditions, a group of doctors, including Marik, founded the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Working Group7 (FLCCC), and began developing a modified protocol specifically for COVID-19.
The original protocol for COVID-19 is detailed in “COVID-19 Critical Care.” Known as the MATH+ protocol,8,9 it involves the use of three key medicines, all of which need to be started within six hours of hospital admission:
- Intravenous methylprednisolone, to suppress the immune system and prevent organ damage from cytokine storms
- Intravenous ascorbic acid (vitamin C), to control inflammation and prevent the development of leaky blood vessels in the lungs
- Subcutaneous heparin (enoxaparin), to thin the blood and prevent blood clots
MATH+ Prophylactic and At-Home Treatment Protocol
The initial MATH+ protocol10 was released in April 2020. In early July and August, it was updated11,12 to include quercetin and a number of optional nutrients and drugs, not only for critical care but also for prophylaxis and mild disease being treated at home.
For prophylaxis, the FLCCC recommends:13
- Vitamin C — 500 mg
- Quercetin — 250 mg to 500 mg
- Zinc — 75-100 mg/day (acetate, gluconate or picolinate). Zinc lozenges are preferred. After one month, reduce the dose to 30 mg to 50 mg per day
- Melatonin (slow release) — Begin with 0.3 mg and increase as tolerated to 2 mg at night
- Vitamin D3 — 1,000 to 4,000 IUs per day
The at-home treatment for mildly symptomatic patients is very similar, but adds several optional drugs, including aspirin (ASA), famotidine (an antacid), ivermectin (a heartworm medication that has been shown to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro14). (For dosages, see the Critical Care Management Protocol15 summary, available on the Easter Virginia Medical School’s site.)
They also recommend monitoring your oxygen saturation with a pulse oximeter and to go to the hospital if you get below 94%. The medical evidence to support each drug and nutrient can be found under “Medical Evidence”16 on the FLCCC’s website.
MATH+ Critical Care In-Hospital Protocol
In July, the in-hospital protocol was revised17 again to include thiamine (which is also a key ingredient in Marik’s sepsis protocol). As of the last revision, the in-hospital MATH+ protocol18 calls for:
- IV methylprednisone
- High-dose ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
- Thiamine
- Heparin
- Optional: melatonin, zinc, vitamin D3, atorvastatin, famotidine and magnesium
According to the FLCCC, “By initiating the protocol soon after a patient meets criteria for oxygen supplementation, the need for mechanical ventilators and ICU beds will decrease dramatically.” While heparin is an important part of the protocol due to the clotting complications in the microvasculature of the lung, it is likely that N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) is likely a far better choice as it is far safer and likely as effective.
The Two Phases of Disease Require Different Treatments
This is a key point: There are two distinct phases or stages of COVID-19 — the viral replication stage and the immune dysfunction stage — and the treatment must be appropriate for the stage you’re in. Equally crucial is starting aggressive treatment as early as possible. The graphic below details the two stages of disease, and the FLCCC’s suggested treatment focus for each.
Peak viral replication takes place at the earliest signs of symptoms, which include cold/flu-like symptoms, loss of taste and smell, myalgia (muscle pain) and general malaise.
From the time of symptom onset to the time that immune dysregulation starts to set in (accompanied by worsening symptoms) is about five or six days. During this time, you need to aggressively treat, whether you’re at home (see the at-home treatment for symptomatic patients) or in the hospital.
The key remedies in this phase are antivirals (which is what vitamin C, quercetin and zinc are). Anti-inflammatories should be avoided in this phase, Marik warns. Again, if treating at home, be sure to monitor your oxygen saturation with a pulse oximeter. If your oxygen drops to 94% or below when sitting or walking, it’s time to go to the hospital.
If your immune system is unable to successfully combat the virus, then five to six days after first symptoms, early pulmonary dysfunction can set in. At this point, anti-inflammatories — i.e., corticosteroids — and immune suppressive therapeutics are required.
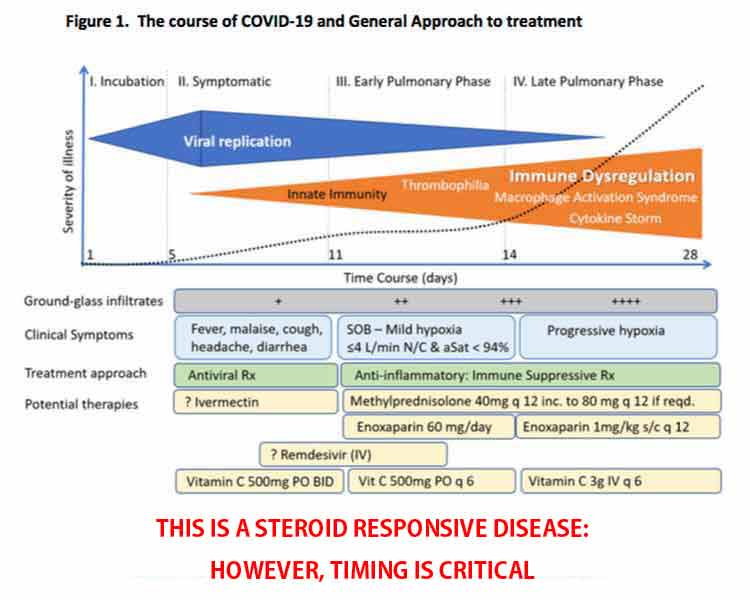
Viral Load Declines as Inflammation Rises
Another important concept explained by Marik in the featured interview is that the inflammatory response rises as the viral load decreases. They do not rise together.
“So, it’s really not the virus that is causing cytopathic effects,” he says. By the time you enter the pulmonary phase of the disease, your viral load has actually significantly decreased, but for some reason the inflammatory response then starts to run amok.
Your oxygen saturation is “the key indicator of pulmonary involvement,” Marik says. Once your oxygen saturation starts to decline, you are entering the early pulmonary phase where inflammation is rapidly increasing.
This is why it’s so important to make sure you’re measuring your oxygen saturation. Do not try to treat at home if your oxygen is dropping. Go to the hospital. Again, early treatment is crucial. Hopefully, your doctor will be willing to implement the MATH+ protocol.
Corticosteroids Are a Crucial Component
In a short essay19 co-written by the entire FLCCC team, they express their conviction that the MATH+ protocol is one of the best, most effective, critical care protocols for COVID-19 to date.
“Months ago, early on in COVID19, the FLCCC created the MATH+ protocol based on our physicians’ insights into COVID19 as a steroid-responsive disease.
This treatment recommendation went against all the major national and international health care societies that had misinterpreted the medical literature, a body of published evidence which, upon careful and deep review, actually supported the use of corticosteroids in prior pandemics …
Thousands of patients who became critically ill with Covid19 and who were suffering from massive inflammation may have been saved if this safe and powerful anti-inflammatory medicine had been provided.”
The essay20 stresses the importance of corticosteroids in the treatment of COVID-19, and cites results from the RECOVERY trial,21,22,23 a large, randomized controlled COVID-19 study by the University of Oxford, that validates their recommendation to use corticosteroids as soon as the patient is hospitalized.
In that study, the corticosteroid dexamethasone improved survival by one-third in ventilated patients and one-fifth in those requiring oxygen. However, the FLCCC believes another type of corticosteroid, methylprednisolone, is a better, more effective, choice.
First, because it reaches higher concentrations in lung tissue, and secondly, because it most closely matches the inflammatory gene activation patterns induced by SARS-CoV-2. They also believe the dexamethasone dose used in the RECOVERY trial was too low, especially for severe cases.
“In the hospitals of two of our FLCCC physicians — each having treated over 100 hospitalized patients with MATH+ often early on in the hospitalization, the hospital mortality rate to date is 7% in one hospital (Dr. Paul Marik, Norfolk, Va.) and less than 1% in the other (Dr. Joseph Varon, Houston, Texas),” the essay states.24
Vitamin C and Quercetin Work Synergistically
June 19, 2020, Marik published the paper,25 “Quercetin and Vitamin C: An Experimental, Synergistic Therapy for the Prevention and Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Related Disease (COVID-19)” in the journal Frontiers in Immunology, which notes:
“Ascorbic acid is a crucial vitamin necessary for the correct functioning of the immune system. It plays a role in stress response and has shown promising results when administered to the critically ill. Quercetin is a well-known flavonoid whose antiviral properties have been investigated in numerous studies.
There is evidence that vitamin C and quercetin co-administration exerts a synergistic antiviral action due to overlapping antiviral and immunomodulatory properties and the capacity of ascorbate to recycle quercetin, increasing its efficacy.
Safe, cheap interventions which have a sound biological rationale should be prioritized for experimental use in the current context of a global health pandemic.”
The paper presents evidence for the use of vitamin C and quercetin — based on their biological actions and pharmacokinetics profiles — both as prophylaxis in high-risk populations, and as an adjunct to drugs such as Remdesivir or convalescent plasma in the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Post-COVID Syndrome
In the interview, Marik also addresses the issue of “post-COVID syndrome,” which he says is very similar to that of post-sepsis syndrome. In some cases, COVID-19 patients have recovered from the infection, only to die due to pulmonary embolism (blood clots in the lungs) or other organ dysfunction.
Marik suspects this is because the inflammatory response is still overactive. Many sepsis patients will have very high cytokine levels even a year after their recovery. He believes steroids are one key to downregulating the inflammatory response, which would prevent this problem.
A good way to screen for this, Marik says, is to measure CRP, which appear to be a good marker for ongoing inflammation. If CRP is high after recovering from COVID-19, Marik suggests doing a short course of corticosteroids to downregulate the inflammatory response. Aspirin may also be helpful if D-dimer is high. These should be used under medical supervision.
I believe this information needs to be shared far and wide, if we are to prevent more people from dying unnecessarily. More and more, as doctors are starting to speak openly about their clinical findings, we see there are quite a few different ways to tackle this illness without novel antivirals or vaccines, using older, inexpensive and readily available medications and nutrients that are already known to be safe.
from Articles https://ift.tt/34sHSri
via IFTTT
You Are Likely Deficient in Choline
July 15, 2020, the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee (DGAC) published its 2020 report, an independent scientific review on the nutrition and health status of Americans, and there was a concerning finding: Most Americans don't get enough choline, an essential nutrient that's vitally important, but rarely discussed.
Marie Caudill, Ph.D., a registered dietitian who is internationally recognized for her research on choline and folate, says the most alarming find from the report is that the populations who would benefit the most from extra choline — pregnant and lactating women, infants and children — are falling especially short.
In pregnant women, choline deficiency is associated with an increased risk of neural tube defects. In the general population, getting too little choline can lead to the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and muscle damage.
What Does Choline Do?
Choline is often lumped in with the B vitamins, but it's not technically a vitamin. It's more of a vitamin-like nutrient.1 Choline helps support optimal health at all stages of life. It plays a role in healthy fetal development, helps maintain cognition and memory, boosts energy, improves fitness and keeps your liver healthy. Your brain and nervous system need adequate amounts of choline to help regulate muscle control, mood and memory.2 Choline is also involved in metabolism. Other roles of choline include:
|
Promoting healthy fetal development3 — Choline is required for proper neural tube closure,4 brain development and healthy vision.5 Research shows mothers who get sufficient choline impart lifelong memory enhancement to their child due to changes in the development of the hippocampus (memory center) of the child's brain.6 Choline deficiency also raises your risk of premature birth, low birth weight and preeclampsia. |
|
Helping reduce the risk for cardiovascular disease — According to a study in the journal ARYA Atherosclerosis, choline may help prevent cardiovascular disease by converting homocysteine to methionine.7 Homocysteine is an amino acid that may increase your risk for heart disease and stroke if it accumulates in the blood.8 |
|
Aiding the synthesis of phospholipids, the most common of which is phosphatidylcholine, better known as lecithin, which constitutes between 40% and 50% of your cellular membranes and 70% to 95% of the phospholipids in lipoproteins and bile.9 |
|
Boosting your nervous system health — Choline is necessary for making acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in healthy muscle, heart and memory performance.10 |
|
Strengthening cell messaging, by producing cell-messaging compounds.11 |
|
Facilitate fat transport and metabolism — Choline is needed to carry cholesterol from your liver, and a choline deficiency could result in excess fat and cholesterol buildup.12 |
|
Modulates DNA synthesis,13 aiding in the process along with other vitamins, such as folate and B12. |
|
Improves cognitive performance — Researchers found a relationship between high dietary choline and better cognitive performance in a study involving men and women from the Framingham Offspring population.14 In a group of 1,391 men and women, performance factors were better in those who consumed more choline, adding to evidence your nutrition makes a difference in how your brain ages. |
|
Helps manage certain mental disorders — Research shows that low choline intake is associated with increased anxiety levels.15 This nutrient has been used in treating rapid-cycling bipolar disorder, too. A study published in the journal Biological Psychiatry shows that choline supplementation helped reduce the manic and mood symptoms of people with bipolar disorder.16 |
|
Influences methylation reactions17 |
|
Aids in healthy mitochondrial function18 |
The Problems With Choline Deficiency
If you don't get enough choline through your diet, it can result in a choline deficiency, which has widespread negative health effects. Because choline is involved in fat metabolism, low levels of the nutrient can result in an overaccumulation of deposits of fat in your liver.19 Eventually, this can lead to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, which currently affect 30% of the U.S. population.20 Choline deficiency can also lead to liver damage and muscle damage.21
Choline deficiency can be even more worrisome for pregnant women and lactating mothers. Choline is essential for proper brain development of a growing fetus. It also helps maintain proper homocysteine concentrations during pregnancy.22
According to a study published in the American Journal of Epidemiology, there is an increased risk of neural tube birth defects in babies of women who consume less than 300 mg of choline per day when compared to pregnant women who get at least 500 mg daily.23
Because choline will be pulled from the mother's blood to supply adequate amounts to the fetus, pregnant and lactating women have higher choline needs, yet only 5% get enough, according to one study.24 In addition to pregnant and lactating women, groups at especially high risk for choline deficiency include:
- Endurance athletes — Endurance exercises, like marathons and triathlons, can deplete choline levels. Studies show that supplementing with choline before these types of stressful exercises can help keep the levels of choline in the blood from getting too low.25,26
- People who drink a lot of alcohol — Excess alcohol consumption can increase your need for more choline while simultaneously increasing your risk of deficiency.27
- Postmenopausal women — Postmenopausal women have lower estrogen concentrations, which can increase the risk of organ dysfunction in response to a low-choline diet.28
- Vegetarians and vegans — Animal foods like beef liver, eggs and krill oil are the highest sources of dietary choline. Because vegetarians and vegans have dietary restrictions that eliminate some or all of these choline-rich foods, it can be more difficult to get an adequate amount of the nutrient through diet alone.29
How Much Choline Do You Need?
Your liver makes some choline, but the amount isn't enough to keep you healthy and prevent the adverse effects of choline deficiency. That's why you need to get adequate amounts through your diet.
The amount of choline you need depends on your age, sex and whether or not you're pregnant or nursing. Here's a general breakdown from the National Institutes of Health30:
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnant Women | Nursing Women |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 to 6 months |
125 mg/day |
125 mg/day |
||
|
7 to 12 months |
150 mg/day |
150 mg/day |
||
|
1 to 3 years |
200 mg/day |
200 mg/day |
||
|
4 to 8 years |
250 mg/day |
250 mg/day |
||
|
9 to 13 years |
375 mg/day |
375 mg/day |
||
|
14 to 18 years |
550 mg/day |
400 mg/day |
450 mg/day |
550 mg/day |
|
19 years and older |
550 mg/day |
425 mg/day |
450 mg/day |
550 mg/day |
Keep in mind, however, that some people have genetic polymorphisms that increase the need for choline and certain ethnic and racial groups are more likely to be affected.31 According to Chris Masterjohn, who has a Ph.D. in nutritional science, eating a diet that's high in (otherwise healthy) saturated fats can also increase your need for choline.32
How to Get More Choline
Grass fed beef liver is the richest dietary source of choline, with 430 mg of choline per 100-gram cooked serving.33 But liver isn't as much a staple on American plates as the second highest source of choline — eggs. One single egg, which weighs around 50 grams, contains 169 mg of choline.34
Here's the catch, though: Most of that choline, or 139 mg, is found in the yolk.35 Egg yolks are also rich in lecithin, a fatty acid that's a precursor for choline. That means if you're still following the outdated and totally misguided advice to eat only the egg whites, you're missing out on a lot of the egg's nutrition.
Krill oil, which comes from krill, a crustacean mainly eaten by whales, penguins and other aquatic creatures, is also a rich source of choline. A 2011 study published in the journal Lipids found 69 choline-containing phospholipids in krill oil.36
Of those phospholipids, 60 were phosphatidylcholine substances, which protect against liver disease (including hepatitis and cirrhosis in alcoholics), reduce digestive tract inflammation and lessen symptoms associated with inflammatory conditions such as ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome.37 Other dietary sources of choline include:38
|
Grass fed beef liver |
Organic pasture raised chicken |
|
Atlantic cod |
|
|
Kidney beans |
|
|
Shitake mushroom |
Cauliflower |
According to the DGAC, most multi-vitamin supplements don't contain sufficient amounts of choline. You can find supplements that contain only choline, but it's always best to try to get what you need through a healthy diet.
from Articles https://ift.tt/2EkqOt1
via IFTTT