Asymptomatic 'Casedemic' Is a Perpetuation of Needless Fear
As coronavirus testing takes place en masse across the U.S., many are questioning whether the tests are accurate enough to trust, especially in people who are asymptomatic. Positive reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) tests have several drawbacks that make mass testing problematic and rife for misleading fearmongering.
For starters, the PCR test is not designed to be used as a diagnostic tool as it cannot distinguish between inactive viruses and “live” or reproductive ones.1 This is a crucial point, since inactive and reproductive viruses are not interchangeable in terms of infectivity. If you have a nonreproductive virus in your body, you will not get sick and you cannot spread it to others.
The PCR Cycle Threshold Matters
Secondly, many if not most laboratories amplify the RNA collected far too many times, which results in healthy people testing “positive.” To understand why the false positive rate for PCR tests is so high, you need to understand how the test works.2
The video above explains how the PCR test works and how we are interpreting results incorrectly. In summary, the PCR swab collects RNA from your nasal cavity. This RNA is then reverse transcribed into DNA. However, because the genetic snippets are so tiny, they must be amplified to become discernible.
Each round of amplification is called a cycle, and the number of amplification cycles used by any given test or lab is called a cycle threshold. Amplification over 35 cycles is considered unreliable and scientifically unjustified. Some experts say nothing above 30 cycles should be used,3 yet Drosten tests and tests recommended by the World Health Organization are set to 45 cycles.4,5,6
When you go above 30 cycles, even insignificant sequences of viral DNA end up being magnified to the point that the test reads positive even if your viral load is extremely low or the virus is inactive and poses no threat to you or anyone else.
‘Casedemic’ Fuels Needless Fear
When labs use these excessive cycle thresholds, you end up with a far higher number of positive tests than you would otherwise. At present, and going back a number of months now, what we’re really dealing with is a “casedemic,”7,8 meaning an epidemic of false positives.
Remember, in medical terminology, when used accurately, a “case” refers to someone who has symptoms of a disease. By erroneously reporting positive tests as “cases,” the pandemic appears magnitudes worse than it actually is.
“The goal is to keep you scared, isolated and demoralized for a purpose,” says PJ Media.9 “Only a beaten nation would stand for what comes next.” And that next step is a reset of America as you know it, with the UN’s one-world Agenda 2030 at the helm. To learn more, be sure to read “What You Need to Know About the Great Reset.”
As reported by Global Research in “The COVID-19 RT-PCR Test: How to Mislead All Humanity. Using a ‘Test’ to Lock Down Society”:10
“Official postulate … positive RT-PCR cases = COVID-19 patients. This is the starting postulate, the premise of all official propaganda, which justifies all restrictive government measures: isolation, confinement, quarantine, mandatory masks, color codes by country and travel bans, tracking, social distances in companies, stores and even, even more importantly, in schools.
This misuse of RT-PCR technique is used as a relentless and intentional strategy by some governments, supported by scientific safety councils and by the dominant media, to justify excessive measures such as the violation of a large number of constitutional rights, the destruction of the economy with the bankruptcy of entire active sectors of society, the degradation of living conditions for a large number of ordinary citizens, under the pretext of a pandemic based on a number of positive RT-PCR tests, and not on a real number of patients.”
COVID Testing Fraud Fuels ‘Casedemic’
In the video at the top of this article, Del Bigtree breaks down how excessively high test sensitivity leads to falsely elevated “case” numbers that in reality mean nothing. He rightly points out that missing from the COVID-19 conversation is the death rate.
“If COVID is a deadly virus, what should we see when cases increase?” he asks. The answer, of course, is an increase in deaths. However, that’s not what’s happening. The two have virtually nothing to do with each other.
In the video, Bigtree features a November 4, 2020, tweet11 by White House coronavirus adviser Dr. Scott Atlas showing the number of positive tests (aka “cases”) in blue and COVID-19 related deaths in red, since the start of the pandemic up until the end of October 2020. As you can see, there’s no correlation between so-called cases and deaths.
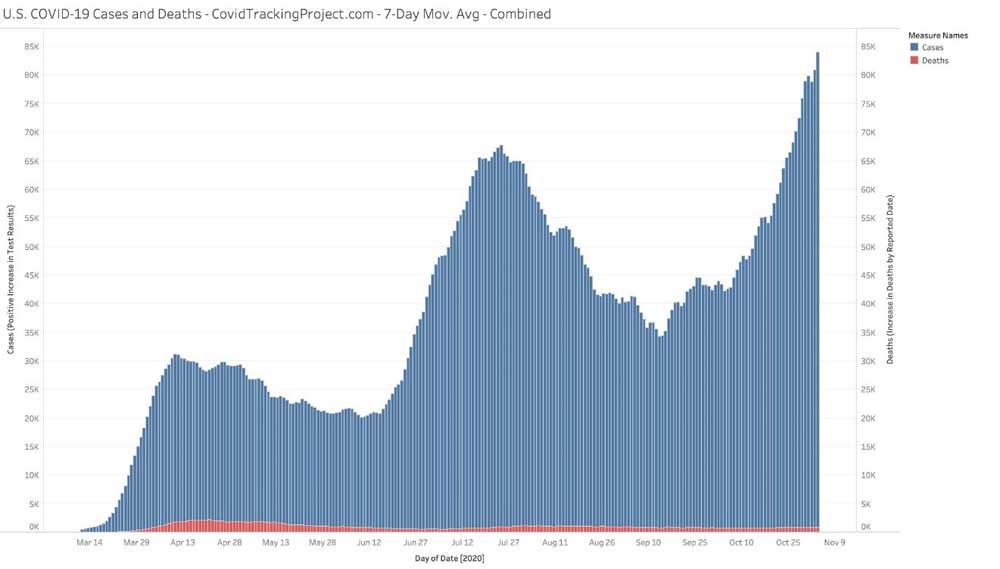
A second graph tweeted12 by Atlas shows the number of U.S. counties reporting more than 10 COVID-19 related deaths per day, based on New York Times data. It too indicates that the death rate is steadily dwindling.

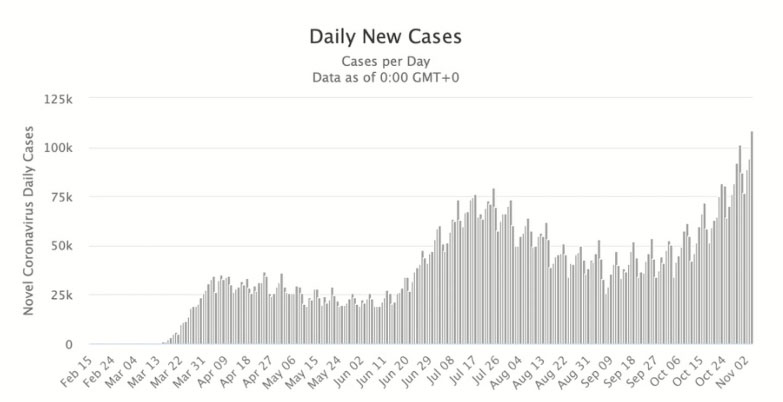
Worldwide, we see the same phenomenon. The first graph below, from Bigtree’s video report, shows the worldwide daily new cases since the beginning of the pandemic. The second graph shows daily COVID-19 related deaths, worldwide. While the number of positive tests have risen, fallen and risen again, the number of deaths have fallen off and do not appear to be rising in tandem with positive test rates any longer.

Shocking Data Reveal Inaccuracy of PCR Tests
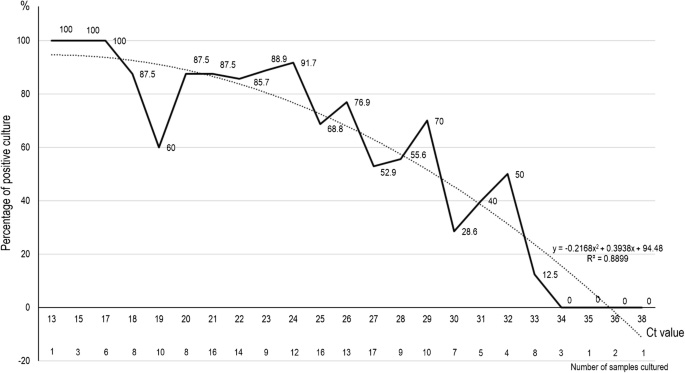
Circling back to the PCR cycle threshold and its influence on positivity rates, Bigtree reviews research13 showing that to really maximize accuracy, PCR tests should use far fewer cycles.
At just 17 cycles, 100% of the positive results were confirmed to be real positives. In other words, 17 cycles would likely be the ideal CT. Above 17 cycles, accuracy drops dramatically. By the time you get to 33 cycles, the accuracy rate is a mere 20%, meaning 80% are false positives. Beyond 34 cycles, your chance of a positive PCR test being a true positive shrinks to zero. This is the graph from that study.14
Other data presented by Bigtree shows that your chances of getting a true positive on the first day of COVID-19 symptom onset is only about 40%. Not until Day 3 from symptom onset do you have an 80% chance of getting an accurate PCR result.
By Day 5 the accuracy shrinks considerably and by Day 8 the accuracy is nil. Now, these are symptomatic people. When you’re asymptomatic, your odds of a positive PCR test being accurate is therefore virtually nonexistent.
Rapid Test Is Less Sensitive and May Be Better for Most
To address some of the shortcomings in PCR testing, most notably the time it takes to get the result, rapid tests have been developed that can provide an answer in minutes. These tests also appear to be less sensitive, which is actually a good thing. One such rapid test, called the Sofia by Quidel, looks for the presence of antigens (coronavirus proteins) rather than RNA.
In a recent comparison of PCR and the Quidel rapid test, University of Arizona researchers discovered that while the rapid test can detect more than 80% of the infections found by slower PCR tests, when used on asymptomatic individuals, that rate dropped to just 32%. (The study has not been published yet but was reviewed by experts solicited by The New York Times.15,16)
While a 32% detection rate may sound terrible, appearances can be deceiving. Remember, if labs are using a cycle threshold (CT) of, say, 40 cycles, the number of positive PCR results will be vastly exaggerated.
According to The New York Times,17 researchers have been “unable to grow the coronavirus out of samples from volunteers whose PCR tests had CT values above 27.” If the virus cannot replicate, you will not get ill and are not infectious, so you cannot spread it to others.
When all PCR tests with a CT value over 30 were excluded from the comparison, the rapid test was found to detect more than 85% of the SARS-CoV-2 infections detected by the PCR tests, and this held true whether the individual had symptoms or not.
Mass Testing Shown To Be Ineffective at Best
Why are we still testing asymptomatic people? According to a study18,19 in the October 21, 2020, issue of PLOS ONE, mass testing is at best ineffective and at worst, harmful.
“Even for highly accurate tests, false positives and false negatives will accumulate as mass testing strategies are employed under pressure, and these misdiagnoses could have major implications on the ability of governments to suppress the virus,” the authors state.20
“The present analysis uses a modified SIR model to understand the implication and magnitude of misdiagnosis in the context of ending lockdown measures. The results indicate that increased testing capacity alone will not provide a solution to lockdown measures. The progression of the epidemic and peak infections is shown to depend heavily on test characteristics, test targeting, and prevalence of the infection.
Antibody based immunity passports are rejected as a solution to ending lockdown, as they can put the population at risk if poorly targeted. Similarly, mass screening for active viral infection may only be beneficial if it can be sufficiently well targeted, otherwise reliance on this approach for protection of the population can again put them at risk.”
In an August 28, 2020, interview with The Post,21 Michael Levitt, Nobel Prize winner and professor of structural biology at Stanford, stated mass testing is “a huge waste of money which could much better go to helping people who have lost their jobs … It’s great for the pharmaceutical companies selling test kits, but it’s not doing anything good.”
Fauci Admits CT Over 35 Renders PCR Test Useless
Even Dr. Anthony Fauci has admitted that the PCR test is useless and misleading when run at “35 cycles or higher.”22 He made this comment in a July 16, 2020, “This Week in Virology” podcast:23
“If you get a cycle threshold of 35 or more … the chances of it being replication-confident are minuscule … You almost never can culture a virus from a 37 threshold cycle … [or] even 36 …”
That then begs the question, why is the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommending the test be run at a CT of 40?24 Why are Drosten tests and tests recommended by the World Health Organization set to 45 cycles? As noted by author and investigative journalist Jon Rappaport:25
“All labs in the U.S. that follow the FDA guideline are knowingly or unknowingly participating in fraud. Fraud on a monstrous level, because… Millions of Americans are being told they are infected with the virus on the basis of a false positive result, and …
The total number of COVID cases in America — which is based on the test — is a gross falsity. The lockdowns and other restraining measures are based on these fraudulent case numbers.
Let me back up and run that by you again. Fauci says the test is useless when it’s run at 35 cycles or higher. The FDA says run the test up to 40 cycles in order to determine whether the virus is there. This is the crime in a nutshell … On the basis of fake science, the country was locked down.”
from Articles https://ift.tt/36Nmywl
via IFTTT