Hydroxychloroquine Protocol Continues Getting Censored
If you thought the publication of positive hydroxychloroquine studies would stop the blatant and reprehensible censorship of this COVID-19 remedy, you were wrong. It’s only getting worse.
July 27, 2020, America’s Frontline Doctors, a group of physicians who have organized to counteract the false narrative that hydroxychloroquine is dangerous and shouldn’t be used for COVID-19, held a press conference outside the Supreme Court of the United States.
After The New York Times filed a complaint with Facebook,1 the video was quickly scrubbed from YouTube and social media platforms, but you can find an archived copy of the transcript2 here. Donald Trump Jr., President Trump’s son, even had his Twitter account suspended for 12 hours after posting the video.3
During the hours it was available, the video garnered more than 14 million views and in excess of 600,000 shares. Speaking for the group were the founder, Dr. Simone Gold, and Drs. Bob Hamilton, Stella Immanuel, Dan Erickson, Joe Ladapo and James Todaro.
Frontline Doctors Speak Out, Crushing the Fear Narrative
After their first press conference was censored, the group held a second press conference4 the following day, blasting Facebook, Twitter and YouTube for their unwarranted censorship of medical information that can save lives and provide relief from the fear gripping the nation.
The group believes it is crucial we begin to balance the fear of the virus against what we know about its progression, treatment and survivability. The physicians that are part of this group first and foremost want everyone to have hope, and to realize that effective treatment is available and that very few people need to die, even if they are infected and develop symptoms.
“We implore you to hear this because this message has been silenced. There are many thousands of physicians who have been silenced for telling the American people the good news about the situation — that we can manage the virus carefully and intelligently. But we cannot live with this spider web of fear that’s constricting our country,” Gold said in the first press conference.
Immanuel, a primary care physician in Houston, Texas, reviewed her personal successes with the hydroxychloroquine regimen, saying she’s treated more than 350 patients with COVID-19, including patients with comorbidities that place them at increased risk for severe illness, complications and death. None has died.
“The result has been the same. I put them on hydroxychloroquine, I put them on zinc, I put them on Zithromax, and they’re all well,” Immanuel said.
Prophylactic Use of Hydroxychloroquine
They also stress that hydroxychloroquine in combination with zinc — just one 200 milligram tablet of hydroxychloroquine every other week with daily zinc — is an effective prophylactic that could be given to anyone at high risk of infection. Immanuel noted:
“I’ve put myself, my staff, and many doctors that I know, on hydroxychloroquine for prevention, because by the very mechanism of action, it works early and as a prophylaxis. We see 10 to 15 COVID patients every day. We give them breathing treatments. We only wear surgical mask. None of us has gotten sick. It works.”
People that might benefit from prophylactic use would include high-risk individuals such as teachers and the elderly. This could facilitate the safe reopening of schools and businesses everywhere.
Children, they point out, are at extremely low risk from the infection, rarely display symptoms, and are very inefficient transmission vectors. Parents rarely contract the infection from their children.
Hydroxychloroquine Is NOT a Magic Bullet
It is also very important to understand that while hydroxychloroquine is a useful tool, it must be used very early in the course of the illness, ideally immediately after exposure, because it works on slowing down viral replication. If the virus has already multiplied, the horse is out of the barn and hydroxychloroquine will likely be ineffective later in the course of the illness.
It’s also worth noting that in areas where hydroxychloroquine is hard to get a hold of, quercetin is likely a more effective and less expensive alternative, as its primary mechanism of action is identical to that of the drug, in addition to having many other anti-inflammatory benefits.
Both are zinc ionophores, meaning they shuttle zinc into the cell. There’s compelling evidence to suggest the primary benefit of this protocol comes from the zinc, which effectively inhibits viral replication. The problem is that zinc does not readily enter cells, which is why a zinc ionophore is needed.
You can learn more about all of this in “Is Quercetin a Safer Alternative to Hydroxychloroquine?” “Quercetin Boosts Interferon Response to Viruses and COVID-19” and “How to Improve Zinc Uptake with Quercetin to Boost Immune Health.”
Molecular hydrogen is another simple remedy that could have excellent therapeutic potential against SARS-CoV-2 infection, as explained by Tyler LeBaron in “How Molecular Hydrogen Can Help Your Immune System.”
And please, remember nebulized peroxide. I recently treated the 40-year-old nephew of my gardening consultant that came down with serious pre-terminal COVID-19. He was already on hydroxychloroquine, zinc, quercetin and prednisone and was getting worse until he started the nebulized peroxide. He miraculously improved immediately after this treatment.
I will share his story and video in an upcoming article. The cost of the treatment was less than one penny and it has virtually no side effects if used at the very low 0.1% concentration.
Attacks Heat Up After Second Press Conference
Apparently, the technocrats making the rules disagree with the group’s message of hope and call for return to normalcy, because the attack on America’s Frontline Doctors quickly escalated from scrubbing online platforms of their video to actually taking down their website, americasfrontlinedoctors.com.
In a July 28, 2020, Twitter post, Dr. James Todaro wrote:5
“Wow. It appears Squarespace took down our website today americasfrontlinedoctors.com. We are reaching a new level of censorship. Do people agree with this?”

According to Todaro,6 Squarespace claims the website violated the company’s Acceptable Use policy “regarding activity that’s false, fraudulent, inaccurate or deceiving.” A new website, americasfrontlinedoctorsummit.com7 was created a couple of days later.
But that’s not all. In a July 30, 2020, Twitter post, Gold stated PayPal had temporarily “limited” the group’s ability to receive donations shortly after the new website was announced. However, it seems the problem has been resolved.
That same day, Gold, an emergency room doctor, announced she’d been fired from her job “for appearing in an embarrassing video.” In a Fox News interview with Tucker Carlson, Gold said she’s hired the libel law firm L. Lin Wood to represent her in potential defamation suits, as media efforts are currently underway to smear her professional reputation.
Yale Professor Agrees: Cure for COVID-19 Already Exists
Dr. Harvey A. Risch, a professor of epidemiology at Yale School of Public Health, is also trying to get the message out about hydroxychloroquine. In a July 23, 2020, Newsweek op-ed, he wrote:8
“I have authored over 300 peer-reviewed publications and currently hold senior positions on the editorial boards of several leading journals.
I am usually accustomed to advocating for positions within the mainstream of medicine, so have been flummoxed to find that, in the midst of a crisis, I am fighting for a treatment that the data fully support but which, for reasons having nothing to do with a correct understanding of the science, has been pushed to the sidelines.
As a result, tens of thousands of patients with COVID-19 are dying unnecessarily … I am referring, of course, to the medication hydroxychloroquine.
When this inexpensive oral medication is given very early in the course of illness, before the virus has had time to multiply beyond control, it has shown to be highly effective, especially when given in combination with the antibiotics azithromycin or doxycycline and the nutritional supplement zinc.”
Risch goes on to cite evidence presented in his May 27, 2020, article9 in the American Journal of Epidemiology, which bears the instructive title: "Early Outpatient Treatment of Symptomatic, High-Risk COVID-19 Patients that Should be Ramped-Up Immediately as Key to the Pandemic Crisis."
In it, he reviews five hydroxychloroquine studies that demonstrate “clear-cut and significant benefits to treated patients.” Since the publication of that paper, another seven studies have been published that support hydroxychloroquine’s use against COVID-19. This includes a study led by Dr. Vladimir Zelenko, which involved 400 high-risk COVID-19 patients, all of whom successfully recovered, as well as:10
“… four studies totaling almost 500 high-risk patients treated in nursing homes and clinics across the U.S., with no deaths; a controlled trial of more than 700 high-risk patients in Brazil, with significantly reduced risk of hospitalization and two deaths among 334 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine; and another study of 398 matched patients in France, also with significantly reduced hospitalization risk,” Risch writes.
Hydroxychloroquine Has a Proven Safety Profile
Risch’s American Journal of Epidemiology paper also reviews large-scale studies demonstrating the safety of the medication.
In his Newsweek article,11 he points out that the adverse event reports cited by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration when it warned hydroxychloroquine might cause cardiac arrhythmia, especially when administered with azithromycin, were generated from tens of millions of patient uses of hydroxychloroquine for long periods of time, often for the chronic treatment of lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
“Even if the true rates of arrhythmia are tenfold higher than those reported, the harms would be minuscule compared to the mortality occurring right now in inadequately treated high-risk COVID-19 patients,” Risch writes.12
“This fact is proven by an Oxford University study of more than 320,000 older patients taking both hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin, who had arrhythmia excess death rates of less than 9/100,000 users … A new paper in the American Journal of Medicine by established cardiologists around the world fully agrees with this.”
Negative Studies Used Toxic Doses
Risch also highlights the fact that all of the studies used to claim hydroxychloroquine is dangerous were actually using toxic doses.
While doctors reporting success with the drug are using standard doses around 200 mg per day for either a few days or maybe a couple of weeks, studies such as the Bill & Melinda Gates-funded13 Recovery Trial used 2,400 mg of hydroxychloroquine during the first 24 hours — three to six times higher than the daily dosage recommended14 — followed by 400 mg every 12 hours for nine more days for a cumulative dose of 9,200 mg over 10 days.
Similarly, the Solidarity Trial,15 led by the World Health Organization, used 2,000 mg on the first day, and a cumulative dose of 8,800 mg over 10 days. These doses are simply too high. More is not necessarily better. Too much, and guess what? You might kill the patient. It’s really unclear as to why these studies used such enormous doses, seeing how the dosages this drug is normally prescribed in, for a range of conditions, never go that high.
Appropriate Dosage Renders Positive Results
Meanwhile, a July 1, 2020, retrospective analysis16,17,18 of 2,541 patients in Michigan found use of hydroxychloroquine alone cut mortality by more than half, from 26.4% to 13.5%. Patients received 400 mg of hydroxychloroquine twice on day 1, followed by 200 mg twice a day for the next four days.
No adverse heart-related events were observed. Hydroxychloroquine in combination with azithromycin had a mortality rate of 20.1%, and azithromycin alone had a mortality rate of 22.4%. The azithromycin was dosed as 500 mg on day 1, followed by 250 mg once a day for the next four days.
According to the authors,19 “The combination of hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin was reserved for selected patients with severe COVID-19 and with minimal cardiac risk factors.” Unfortunately, zinc was not included in this trial. A majority of doctors using a hydroxycholoroquine regimen do use zinc, plus an antibiotic to stifle secondary bacterial infections.
“Physicians who have been using these medications in the face of widespread skepticism have been truly heroic,” Risch writes.20 “They have done what the science shows is best for their patients, often at great personal risk.
I myself know of two doctors who have saved the lives of hundreds of patients with these medications, but are now fighting state medical boards to save their licenses and reputations. The cases against them are completely without scientific merit …
As all know, the medication has become highly politicized. For many, it is viewed as a marker of political identity, on both sides of the political spectrum. Nobody needs me to remind them that this is not how medicine should proceed.
We must judge this medication strictly on the science. When doctors graduate from medical school, they formally promise to make the health and life of the patient their first consideration, without biases of race, religion, nationality, social standing — or political affiliation. Lives must come first …
Reality demands a clear, scientific eye on the evidence and where it points. For the sake of high-risk patients, for the sake of our parents and grandparents, for the sake of the unemployed, for our economy and for our polity, especially those disproportionally affected, we must start treating immediately.”
Many Countries Have Successfully Quelled COVID-19
If you want to review more studies on hydroxychloroquine, check out c19study.com,21 which at the time of this writing included the following graphic showing the adjusted death toll in countries that adopted the use of hydroxychloroquine early on, compared to those that did or have not.
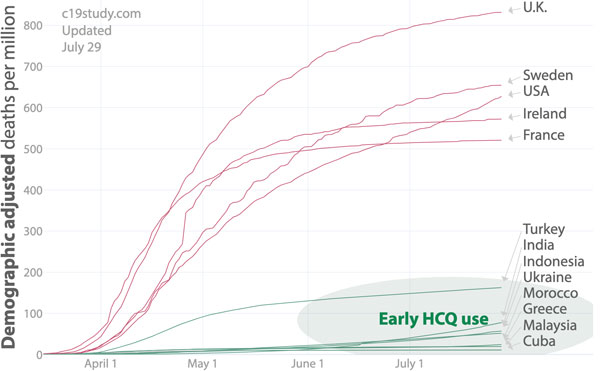
As indicated above, a number of countries have successfully relied on hydroxychloroquine to quell the COVID-19 pandemic, including Dharavi, India, one of the densest slums in the world. As reported by Life Site News:22
“Reports credit the huge turnaround to various factors. Most focused on Dharavi's use of widespread testing and contact tracing … But they ignored the policy most responsible. Indian doctors used hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) for prophylaxis (preventive) treatment — the same drug the American media have politicized.
Dharavi's COVID-19 infection rate dropped drastically from April through June. In July, new infections were very low, almost reaching zero on July 9. Officials have credited23 this turnaround to ‘[a] combination of hydroxychloroquine, vitamin D, and zinc tablets along with homeopathic medicines.’"
In one international poll24,25 of 6,227 doctors in 30 countries, 37% rated the anti-malaria drug hydroxychloroquine as “the most effective therapy” for COVID-19. The poll was done by Sermo, the world’s largest healthcare data collection company and social platform for physicians.
In Spain, where the drug was used by 72% of doctors, it was rated “the most effective therapy” by 75% of them. The typical dose used by a majority of doctors was 400 mg per day.
In the May, 2020, issue of Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease, French microbiologist and infectious disease expert Didier Raoult, founder and director of the research hospital Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire Méditerranée Infection,26 reported27,28 that a combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin, administered immediately upon diagnosis, led to recovery and “virological cure” in 91.7% of patients.
According to Raoult, the drug combination “avoids worsening and clears virus persistence and contagiosity in most cases.” No cardiac toxicity was observed using a dose of 200 mg three times a day for 10 days, along with 500 mg of azithromycin on day 1 followed by 250 mg daily for the next four days.
Chloroquine Inhibits SARS — Known Since 2005
Remarkably, evidence that hydroxychloroquine could be useful against SARS-CoV-2 goes as far back as 2005, when the article29 “Chloroquine Is a Potent Inhibitor of SARS Coronavirus Infection and Spread” was published in the Virology Journal.
Did Dr. Anthony Fauci, appointed to lead the White House Pandemic Response Team, know about this? One could argue he should have. And, if he did, why didn’t he say something? According to this study:30
“… chloroquine has strong antiviral effects on SARS-CoV infection of primate cells. These inhibitory effects are observed when the cells are treated with the drug either before or after exposure to the virus, suggesting both prophylactic and therapeutic advantage.”
In other words, chloroquine functions as both a prophylactic (prevention) and a treatment against SARS coronavirus. This is precisely what many doctors have found with hydroxychloroquine as well, a drug that is very similar to chloroquine but has a safer profile, when used against SARS-CoV-2.
Other early evidence has been highlighted by Raoult. In its April 13, 2020, issue, the German magazine Blauer Bote31,32 lists a collection of 75 expert opinions about the COVID-19 threat. Among them is Raoult, who said (translated from German):
“I did a scientific study on chloroquine and viruses that was published thirteen years ago. Since then, four other studies by other authors have shown that the coronavirus responds to chloroquine. None of this is new.
It takes my breath away that the group of decision-makers doesn't even know about the latest science. We knew about the possible effect of chloroquine on cultured virus samples. It was known to be an effective antiviral.”
A Coordinated Effort to Inhibit Use of an Effective Drug?
The wildly divergent views on hydroxychloroquine appear to have little to do with its safety and effectiveness against COVID-19, and more to do with a concerted and coordinated effort to prevent its use.
There are several reasons for why certain individuals and companies might want to discourage the use of an inexpensive generic drug to work against this pandemic illness.
One of the most obvious reasons is because it might eliminate the need for a vaccine or other antiviral medication currently under development.33 Hundreds of millions of dollars have already been invested, and vaccine makers are hoping for a payday in the billions if not trillions of dollars. In a June 27, 2020, blog post, Dr. Meryl Nass points out:34
“It is remarkable that a series of events taking place over the past three months produced a unified message about hydroxychloroquine … Hydroxychloroquine has been used safely for 65 years in many millions of patients.
And so the message was crafted that the drug is safe for its other uses, but dangerous when used for COVID-19. It doesn’t make sense, but it seems to have worked. Were these acts carefully orchestrated? You decide.
Might these events have been planned to keep the pandemic going? To sell expensive drugs and vaccines to a captive population? Could these acts result in prolonged economic and social hardship, eventually transferring wealth from the middle class to the very rich?”
The fight over hydroxychloroquine may also have political underpinnings, as noted not only by Risch but also by investigative reporter Sharyl Attkisson. In a May 18, 2020, Full Measure report (above), she states that “never before has a discussion about choices of medicine been so laced with political overtones.”
As cautioned by Risch, medicine must not become politicized, especially not during a pandemic. We cannot afford such folly. By politicizing it, the media has taken on a role that can readily be likened to agents of genocide. Naturally, those of us in the holistic field have been aware of how censorship lead people astray, health wise, for a very long time. Conventional doctors are just now getting a taste of what it’s like, and clearly, many are absolutely floored by it.
It’s certainly understandable, because to censor potentially lifesaving medical treatment during a global pandemic really brings it to a whole new level. To so thoroughly demonize a medication that has been used for decades, and could have saved thousands, if not tens of thousands, is as inexcusable as it is inappropriate. Time will tell whether we’ll ever see a time where science is allowed to take its rightful place in medicine again.
from Articles https://ift.tt/3ijNGan
via IFTTT