Majority of People Are Already Resistant to SARS-CoV-2
According to research1 conducted in Switzerland, SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies are only found in the most severe cases — about 1 in 5. That suggests COVID-19 may in fact be five times more prevalent than suspected. It also means it may be five times less deadly than predicted.
The study,2 “Systemic and Mucosal Antibody Secretion Specific to SARS-CoV-2 During Mild Versus Severe COVID-19,” was posted on the prepublication server bioRxiv, May 23, 2020. According to the authors:
“When symptomatic, COVID-19 can range from a mild flu-like illness in about 81% to a severe and critical disease in about 14% and 5% of affected patients, respectively.”
The Swiss study,3 which sought to investigate SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody responses, found that even though people who had been exposed to infected individuals had SARS-CoV-2-specific immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies in their mucosa, there were no virus-specific antibodies in their blood.
IgA is an antibody that plays a crucial role in the immune function of your mucous membranes, while IgG is the most common antibody that protects against bacterial and viral infections and is found in blood and other bodily fluids. As explained by the authors:4
“As with other coronaviruses, symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 disease causes an acute infection with activation of the innate and adaptive immune systems. The former leads to the release of several pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-6 …
Subsequently, B and T cells become activated, resulting in the production of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies, comprising immunoglobulin M (IgM), immunoglobulin A (IgA), and immunoglobulin G (IgG).
Whereas coronavirus-specific IgM production is transient and leads to isotype switch to IgA and IgG, these latter antibody subtypes can persist for extended periods in the serum and in nasal fluids. Whether SARS-CoV-2-specific IgG antibodies correlate with virus control is a matter of intense discussions.”
Antibody Response Dependent on Severity
In COVID-19-positive patients with mild symptoms, SARS-CoV-2-specific IgA titers turned positive an average of eight days after onset of symptoms and were mostly transient. In some cases, however, IgA were completely absent. Serum IgG levels either remained negative, or reached positive values nine to 10 days after symptom onset.
In patients with severe symptoms, a “highly significant” increase of both SARS-CoV-2-specific serum IgA titers were found on day three or four, and even more pronounced IgG titers were present on day four or five. Both were independent of age or comorbidities. Only in severe cases of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) were “very high” levels of IgA found. According to the authors:5
“Interestingly, some of the SARS-CoV-2-exposed healthcare workers with negative SARS-CoV-2-specific IgA and IgG serum titers had detectable SARS-CoV-2-specific IgA antibodies in their nasal fluids and tears. Moreover, SARS-CoV-2-specific IgA levels in nasal fluids of these healthcare workers were inversely correlated with patient age.
These data show that systemic IgA and IgG production against SARS-CoV-2 develops mainly in severe COVID-19, with very high IgA levels seen in patients with severe ARDS, whereas mild disease may be associated with transient serum titers of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies but stimulate mucosal SARS-CoV-2-specific IgA secretion. The findings suggest four grades of antibody responses dependent on COVID-19 severity …
We think these findings suggest a model where the extent and duration of SARS-CoV-2-related clinical symptoms, which likely correlates with virus replication, dictates the level of virus-specific humoral immunity.
This hypothesis is consistent with previous publications demonstrating that the magnitude of the humoral response toward SARS-CoV-2 is dependent on the duration and magnitude of viral antigen exposure.
Low antigen exposure will elicit mucosal IgA-mediated responses, which can be accompanied by systemic IgA production; however, systemic virus-specific IgA responses can also be absent, transient or delayed. This type of ‘mucosal IgA’ antibody response seemed to be particularly prevalent in younger individuals with mild SARS-CoV-2 infection without evidence of pneumonia.”
The Young Have Greater Mucosal Immunity Than the Old
The Swiss researchers suggest these findings could be “a reflection of increased mucosal immunity in the young or decreased mucosal immunity in the old.” They point out previous data showing HKU1-specific IgG — antibodies responding to another type of coronavirus that causes the common cold — are absent in people under the age of 20, while higher levels of these antibodies are found in older people.
Extrapolation suggests infants and children “have primed mucosal innate and IgA antibody responses due to their frequent upper respiratory tract infections and, therefore, respond preferentially in this manner to SARS-CoV-2 infection,” the researchers state.
On the other hand, studies have shown the strength of antiviral immune responses, including T cell activation and proliferation, slows with age. This can partially explain why older people are vastly more susceptible to severe COVID-19 illness and death. Other factors like vitamin D levels and immunosenescence that increases in the elderly are also likely important.
Mortality Is a Fraction of What Was Predicted
As noted in an article on Off-Guardian.com, which reported the results of the Swiss study:6
“… if the authors are indeed correct in their estimation, this might mean SARS-COV-2’s infection rate (IFR) would need to be revised downward yet again. If 80% of those infected really do not produce antibodies then there is a live possibility the virus is present in many more people than usually supposed. Which would in turn potentially reduce the IFR, possibly considerably.
In the early stages, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated the virus’ IFR to be as high as 3.4%. The models based on those numbers have, however, been shown to be wildly inaccurate …
Dissenting experts7 appear to have been vindicated by the serological studies, using blood tests looking for Sars-Cov-2 antibodies done across different populations all over the world, which routinely suggest that the IFR is closer to 0.3%8 than the WHO’s initial figure of 3.4%.
From Japan to Iceland to Los Angeles, the numbers returned were between 0.06 and 0.4. Within the range of seasonal influenza. As a result of these studies, the U.S. CDC’s most recent ‘estimated IFR’ is between 0.26% and 0.4%.9 Roughly 1/10th of the initial estimates.”
Innate and Adaptive Immunity
For clarity, it’s important to realize you have two types of immunity. Your innate immune system is primed and ready to attack foreign invaders at any moment and is your first line of defense. Your adaptive immune system,10 on the other hand, “remembers” previous exposure to a pathogen and mounts a response when an old foe is recognized.
Your adaptive immune system is further divided into two arms: humoral immunity (B cells) and cell mediated immunity (T cells). The B cells and T cells are manufactured as needed from specialized stem cells. The graphs below are from my Vitamin D document and will help you understand the components of these systems and their timing.
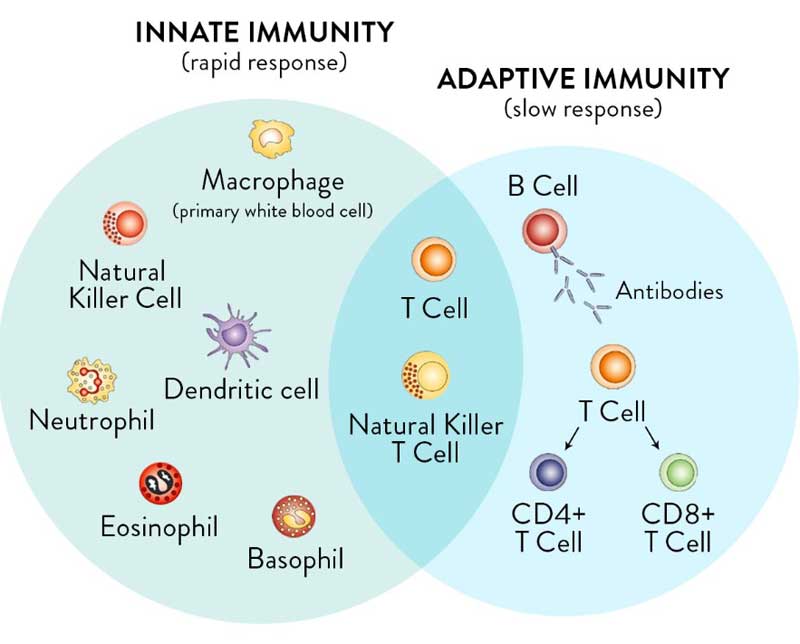
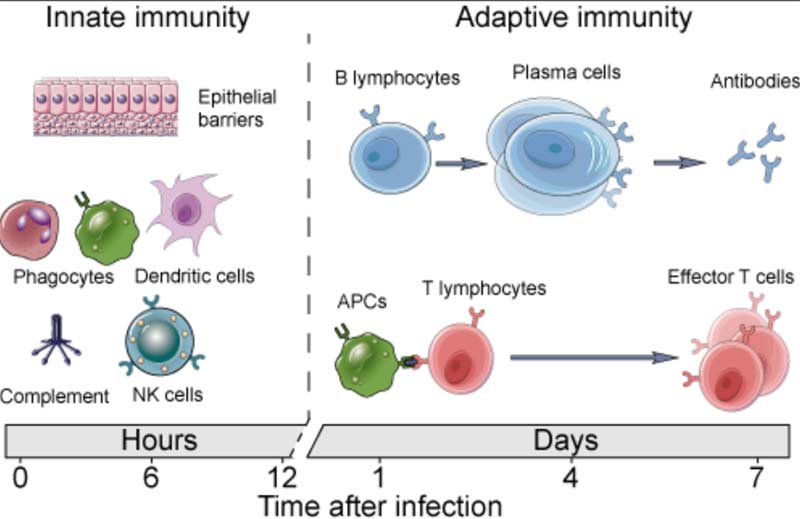
If you have never been exposed to a disease but are given antibodies from someone who got sick and recovered, you can gain humoral immunity against that disease. Your humoral immune system can also kick in if there’s cross-reactivity with another very similar pathogen.
In the case of COVID-19, there’s evidence11 to suggest exposure to other coronaviruses that cause the common cold can confer immunity against SARS-CoV-2.
Majority Resistant to COVID-19 Even Without Exposure
One such study12,13 was published May 14, 2020, in the journal Cell. It found 70% of samples obtained by the La Jolla Institute for Immunology from patients who had recovered from mild cases of COVID-19 had resistance to SARS-CoV-2 on the T-cell level.
Curiously, 40% to 60% of people who had not been exposed to SARS-CoV-2 also had resistance to the virus on the T-cell level. According to the authors, this suggests there’s “cross-reactive T cell recognition between circulating ‘common cold’ coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2.” In other words, if you’ve recovered from a common cold caused by a particular coronavirus, your humoral immune system may activate when you encounter SARS-CoV-2, thus rendering you resistant to COVID-19.
May 14, 2020, Science magazine reported14 these Cell findings, drawing parallels to another earlier paper15 by German investigators that had come to a similar conclusion. That German paper,16 the preprint of which was posted April 22, 2020, on Medrxiv, found helper T cells that targeted the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in 15 of 18 patients hospitalized with COVID-19. As reported by Science:17
“The teams also asked whether people who haven’t been infected with SARS-CoV-2 also produce cells that combat it. Thiel and colleagues18 analyzed blood from 68 uninfected people and found that 34% hosted helper T cells that recognized SARS-CoV-2.
The La Jolla team19 detected this crossreactivity in about half of stored blood samples collected between 2015 and 2018, well before the current pandemic began …
The results suggest ‘one reason that a large chunk of the population may be able to deal with the virus is that we may have some small residual immunity from our exposure to common cold viruses,’ says viral immunologist Steven Varga of the University of Iowa. However, neither of the studies attempted to establish that people with crossreactivity don’t become as ill from COVID-19.
Before these studies, researchers didn’t know whether T cells played a role in eliminating SARS-CoV-2, or even whether they could provoke a dangerous immune system overreaction. ‘These papers are really helpful because they start to define the T cell component of the immune response,’ [Columbia University virologist Angela] Rasmussen says.”
Herd Immunity Theory May Need Revision
Now, if it’s true that a majority are already resistant to COVID-19 due to previous exposure to other coronaviruses, then we’ve probably already reached the threshold for herd immunity, and vaccinating every human on the planet (or close to it) will not be necessary. In fact, it’s starting to look as though a vaccine may be entirely moot.
This research also hints at the possibility that herd immunity isn’t what we think it is. The cross-reactivity on the T cell level seen with SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses may also exist for other viruses.
On the flip side, there’s a phenomenon known as viral interference, where exposure to one virus makes you more susceptible to another virus. Research20 has found that those who received the influenza vaccine were 36% more susceptible to coronavirus infection. This too may be playing a role in COVID-19 deaths among the elderly, since most who reside in nursing homes are given the flu vaccine each year.
Long-Term Immunity Against COVID-19 Appears Prevalent
Yet another study,21,22,23 this one by researchers in Singapore, found common colds caused by the betacoronaviruses OC43 and HKU1 might make you more resistant to SARS-CoV-2 infection, and that the resulting immunity might last as long as 17 years.
In addition to the common cold, OC43 and HKU1 — two of the most commonly encountered betacoronaviruses24 — are also known to cause bronchitis, acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pneumonia in all age groups.25 As reported by the Daily Mail:26
“They share many genetic features with the coronaviruses Covid-19, MERS and SARS, all of which passed from animals to humans. Coronaviruses are thought to account for up to 30 percent of all colds but it is not known specifically how many are caused by the betacoronavirus types.
Now scientists have found evidence that some immunity may be present for many years due to the body's 'memory' T-cells from attacks by previous viruses with a similar genetic make-up — even among people who have had no known exposure to Covid-19 or SARS …
Blood was taken from 24 patients who had recovered from Covid-19, 23 who had become ill from SARS and 18 who had never been exposed to either SARS or Covid-19 …
Half of patients in the group with no exposure to either Covid-19 or SARS possessed T-cells which showed immune response to the animal betacoronaviruses, Covid-19 and SARS. This suggested patients' immunity developed after exposure to common colds caused by betacoronavirus or possibly from other as yet unknown pathogens.”
In other words, if you’ve beat a common cold caused by a OC43 or HKU1 betacoronavirus in the past, you may have a 50/50 chance of having defensive T-cells that can recognize and help defend against SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19. According to the researchers:27
“These findings demonstrate that virus-specific memory T-cells induced by betacoronavirus infection are long-lasting, which supports the notion that Covid-19 patients would develop long-term T-cell immunity. Our findings also raise the intriguing possibility that infection with related viruses can also protect from or modify the pathology caused by SARS-Cov-2.”
Support Offered by Updated Statistical Models
All of these studies add support to the latest COVID-19 mortality models suggesting there is in fact widespread resistance and prior immunity. Freddie Sayers, executive editor of UnHerd, recently interviewed professor Karl Friston, a statistician whose expertise is mathematical modeling, who believes prior immunity across the global population might be as high as 80%.28
Friston is credited with inventing the statistical parametric mapping technique, which is now the standard for understanding brain imaging. As the pandemic erupted, he began applying this method of analysis (which he refers to as “dynamic causal modelling”) to COVID-19 data, coming up with a model that predicts far lower mortality rates than earlier models.
The reason for this is because the “effective susceptible population,” meaning those who are not already immune to COVID-19 and therefore at risk of infection, was never 100%. At most, it was 50% and most likely only around 20%.
Friston’s model effectively vaporizes claims that social distancing is necessary, because once sensible behaviors such as staying home when sick are entered into it, the positive effect of lockdown efforts on “flattening the curve” simply vanish. In all likelihood, the global lockdowns were completely unnecessary, and certainly should not continue, now or in the future.
COVID-19 Growth Projections Were All Wrong
Support for Friston’s model comes from Michael Levitt,29 a professor of structural biology at the Stanford School of Medicine who received the Nobel Prize in 2013 for his development of multiscale models for complex chemical systems.
According to Levitt, statistical data reveal a mathematical pattern that has stayed consistent regardless of the government interventions implemented. While early models predicted an exponential explosion of COVID-19 deaths, those predictions never materialized. As reported by Sayers in the video above:
“After around a two-week exponential growth of cases (and, subsequently, deaths) some kind of break kicks in, and growth starts slowing down. The curve quickly becomes ‘sub-exponential.’ This may seem like a technical distinction, but its implications are profound.
The ‘unmitigated’ scenarios modelled by (among others) Imperial College, and which tilted governments across the world into drastic action, relied on a presumption of continued exponential growth …
But Professor Levitt’s point is that that hasn’t actually happened anywhere, even in countries that have been relatively lax in their responses.”
Levitt believes prior immunity plays a significant role in why we simply don’t see an exponential growth pattern of COVID-19 deaths, and that certainly seems to make sense in light of the studies reviewed above. A majority of people simply aren’t (and weren’t) susceptible to COVID-19.
According to Levitt, the indiscriminate lockdowns implemented around the world were “a huge mistake.” He believes a more rational approach would have been to protect and isolate the elderly, who are by far the most vulnerable and make up the bulk of COVID-19 deaths around the world.
How to Mitigate COVID-19 Risks Further
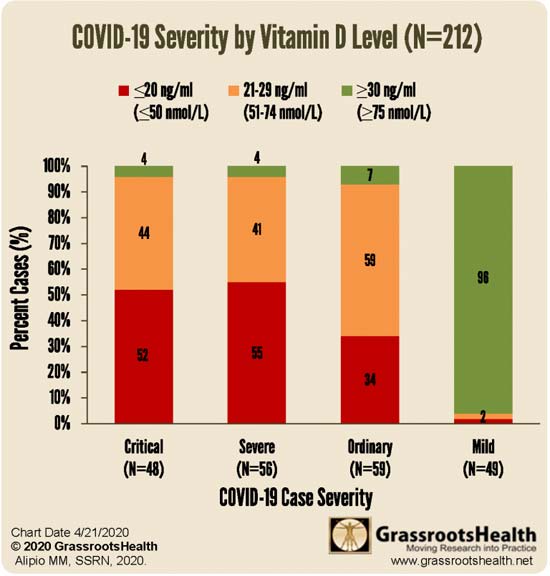
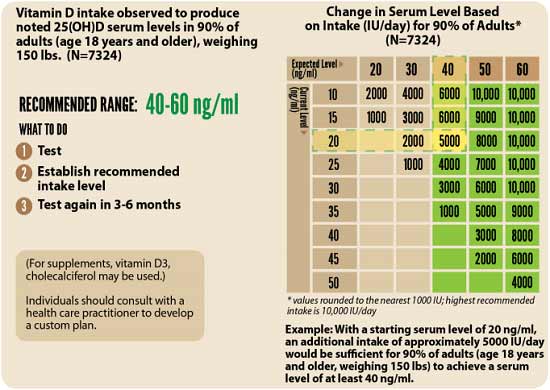
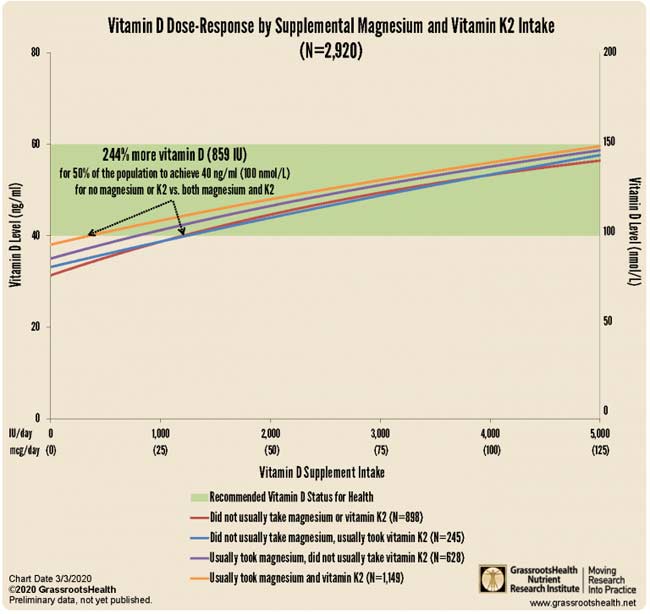
Now, while the risks associated with COVID-19 may be far more insignificant than feared for a majority of the population, they still exist for a minority. The elderly are clearly at greatest risk for severe infection and death, but African-American, Asian and other darker-skinned individuals are also susceptible, likely due to the fact that they tend to have lower vitamin D levels.
To bolster your immune system and lower your risk of COVID-19 infection in the future, be sure to follow the instructions given in “Your Vitamin D Level Must Reach 60 ng/mL Before the Second Wave.” This is particularly true if you or someone you love is elderly or has darker skin. By addressing widespread vitamin D deficiency, we can significantly lower the COVID-19 mortality rate in the future. But we need to start now.

>>>>> Click Here <<<<<
from Articles https://ift.tt/2YLqqek
via IFTTT