Majority Are Already Immune Against SARS-CoV-2
The more data becomes available about SARS-CoV-2, the more obvious it becomes that the response to this pandemic has been grossly overblown. Fatality statistics1,2,3,4,5,6,7 from multiple sources, calculated in a variety of ways, show the risk of dying from COVID-19 is lower than your risk of dying from conventional influenza, at least if you're under the age of 60.
Overall, the data8,9 also show that the overall all-cause mortality has remained steady this year and doesn't veer from the norm. In other words, COVID-19 has not killed off more of the population than would have died in any given year anyway.
Several studies also suggest immunity against SARS-CoV-2 infection is far more widespread than anyone imagined, and that the threshold for herd immunity is far lower than previously estimated.
Most Are Already Immune to SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Studies supporting the claim that widespread immunity against SARS-CoV-2 already exists include:
• Cell, June 202010,11 — This study found 70% of samples from patients who had recovered from mild cases of COVID-19 had resistance to SARS-CoV-2 on the T-cell level. Importantly, 40% to 60% of people who had not been exposed to SARS-CoV-2 also had resistance to the virus on the T-cell level.
According to the authors, this suggests there's "cross-reactive T cell recognition between circulating 'common cold' coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2." In other words, if you've recovered from a common cold caused by a particular coronavirus, your humoral immune system may activate when you encounter SARS-CoV-2, thus rendering you resistant to COVID-19.
• Nature Immunology, September 202012 — This German study was initially posted on a preprint server in June 2020 under the title, "SARS-CoV-2 T-cell Epitopes Define Heterologous and COVID-19-Induced T-Cell Recognition."13
It's now published in the September 2020 issue of Nature Immunology with the slightly altered title, "SARS-CoV-2-Derived Peptides Define Heterologous and COVID-19-Induced T Cell Recognition."14 Much like the Cell study above, this investigation also found that that:
"Cross-reactive SARS-CoV-2 peptides revealed pre-existing T cell responses in 81% of unexposed individuals and validated similarity with common cold coronaviruses, providing a functional basis for heterologous immunity in SARS-CoV-2 infection."
In other words, even among those who were unexposed, 81% were resistant or immune to SARS-CoV-2 infection. The term "heterologous immunity" refers to immunity that develops against a given pathogen after you've been exposed to a nonidentical pathogen.
Typically, this occurs when viruses are sufficiently similar or from closely related species. In this case, SARS-CoV-2 appears to be sufficiently similar to coronaviruses that cause the common cold, so that if you've been exposed to any of those coronaviruses, your immune system is also able to combat SARS-CoV-2.
• The Lancet Microbe, September 202015,16 — This study found that rhinovirus infection, responsible for the common cold, largely prevented concurrent influenza infection by triggering the production of natural antiviral interferon.
The researchers speculate that the common cold virus could potentially help protect against SARS-CoV-2 infection as well. Interferon is part of your early immune response, and its protective effects last for at least five days, according to the researchers. Co-author Dr. Ellen Foxman told UPI:17
"Infection with the common cold virus protected cells from infection with a more dangerous virus, the influenza virus, and [this] occurred because the common cold activated the body's general antiviral defenses.
This may explain why the flu season, in winter, generally occurs after the common cold season, in autumn, and why very few people have both viruses at the same time. Our results show that interactions between viruses can be an important driving force dictating how and when viruses spread through a population.
Since every virus is different, we still do not know how the common cold season will impact the spread of COVID-19, but we now know we should be looking out for these interactions."
• Nature, July 202018,19,20 — Originally posted on a preprint server in May 2020,21 this Singaporean study was published in the July 2020 issue of Nature.22 Here, they found that common colds caused by the betacoronaviruses OC43 and HKU1 might make you more resistant to SARS-CoV-2 infection, and that the resulting immunity could potentially be long-lasting.
Patients who recovered from SARS infection back in 2003 still had T cell reactivity to the N protein of SARS-CoV now, 17 years later. These patients also had strong cross-reactivity to the N protein of SARS-CoV-2.
The authors suggest that if you've beaten a common cold caused by a OC43 or HKU1 betacoronavirus in the past, you may have a 50/50 chance of having defensive T-cells that can recognize and help defend against SARS-CoV-2. According to the authors:
"These findings demonstrate that virus-specific T cells induced by infection with betacoronaviruses are long-lasting, supporting the notion that patients with COVID-19 will develop long-term T cell immunity.
Our findings also raise the possibility that long-lasting T cells generated after infection with related viruses may be able to protect against, or modify the pathology caused by, infection with SARS-CoV-2."
• Cell August 202023,24 — This Swedish study, initially posted on a preprint server in June 202025 and now published in the October 2020 issue of the journal Cell,26 found that SARS-CoV-2-specific memory T cells likely provide long-term immune protection against COVID-19. According to the authors:27
"Acute-phase SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells displayed a highly activated cytotoxic phenotype that correlated with various clinical markers of disease severity, whereas convalescent-phase SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells were polyfunctional and displayed a stem-like memory phenotype.
Importantly, SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells were detectable in antibody-seronegative exposed family members and convalescent individuals with a history of asymptomatic and mild COVID-19.
Our collective dataset shows that SARS-CoV-2 elicits broadly directed and functionally replete memory T cell responses, suggesting that natural exposure or infection may prevent recurrent episodes of severe COVID-19."
Innate and Adaptive Immunity
It's important to realize you have two types of immunity. Your innate immune system is primed and ready to attack foreign invaders at any moment and is your first line of defense. Your adaptive immune system,28 on the other hand, "remembers" previous exposure to a pathogen and mounts a response when an old foe is recognized.
Your adaptive immune system is further divided into two arms: humoral immunity (B cells) and cell mediated immunity (T cells). The B cells and T cells are manufactured as needed from specialized stem cells. The graphs below are from my vitamin D report and will help you understand the components of these systems and their timing.
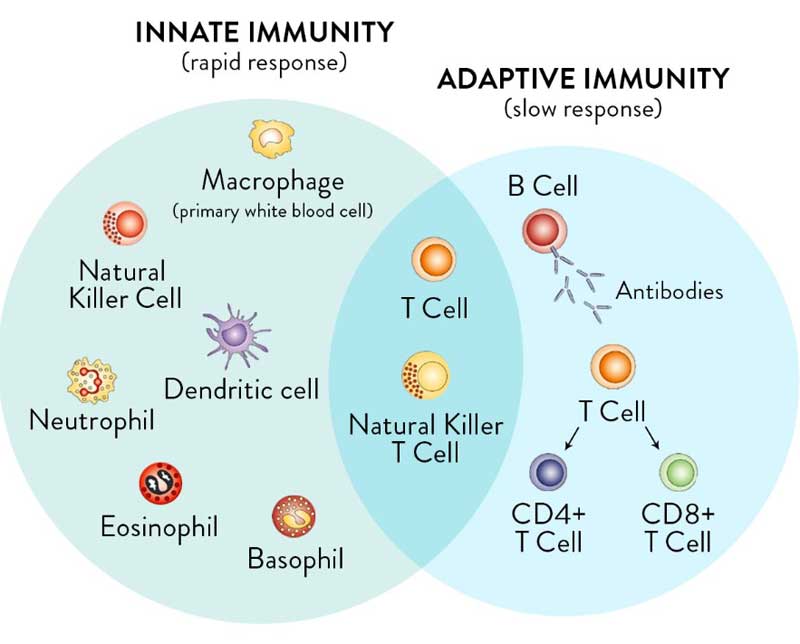
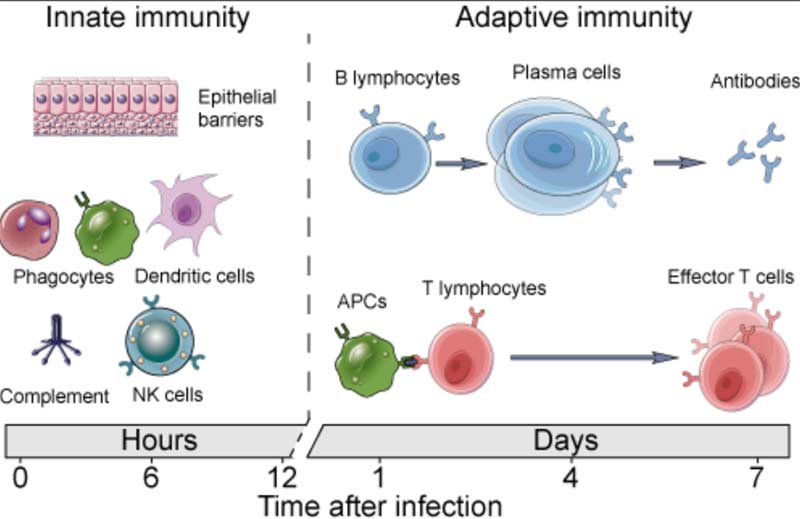
If you have never been exposed to a disease but are given antibodies from someone who got sick and recovered, you can gain humoral immunity against that disease. Your humoral immune system can also kick in if there's cross-reactivity with another very similar pathogen.
As you can see from the list above, in the case of COVID-19, evidence29 suggests exposure to other coronaviruses that cause the common cold can confer immunity against SARS-CoV-2.
On the flip side, there's a phenomenon known as viral interference, where exposure to one virus makes you more susceptible to another virus. Importantly, research30 has found that those who received the influenza vaccine were 36% more susceptible to coronavirus infection.
Mathematical Models Add Support for Widespread Immunity
If it's true that a majority already have some measure of immunity against COVID-19 due to previous exposure to other coronaviruses, then we've probably already reached the threshold for herd immunity, and vaccinating every human on the planet (or close to it) will not be necessary.
Added support for the idea that herd immunity may already have been achieved in most countries comes from statisticians working with mathematical models. In June 2020, Freddie Sayers, executive editor of UnHerd, interviewed31 professor Karl Friston, a statistician who claims immunity against SARS-CoV-2, globally, might be as high as 80%, as reviewed in the video interview above.
Friston is credited with inventing a statistical parametric mapping technique that is now the standard for understanding brain imaging. As the pandemic erupted, he began applying this method of analysis (which he refers to as "dynamic causal modeling") to COVID-19 data, coming up with a model that predicts far lower mortality rates than earlier models.
The reason for this is because the "effective susceptible population," meaning those who are not already immune to COVID-19 and therefore at risk of infection, was never 100%. At most, it was 50% and most likely only around 20%.
Friston's model effectively vaporizes claims that social distancing is necessary, because once sensible behaviors such as staying home when sick are entered into it, the positive effect of lockdown efforts on "flattening the curve" simply vanish. In all likelihood, the global lockdowns were completely unnecessary, and certainly should not continue, now or in the future.
Signs of Herd Immunity Emerge in Sweden
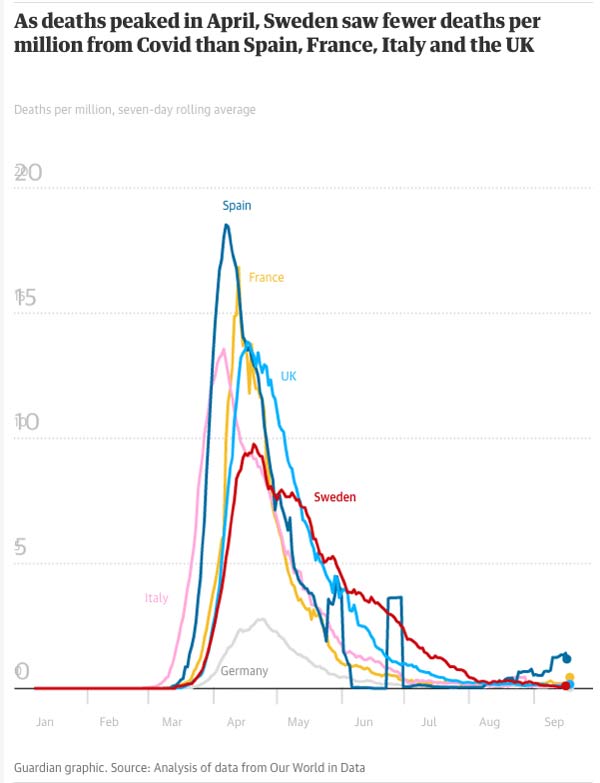
One country that bucked the global lockdown trend was Sweden, and they now appear to be head and neck ahead of most other countries in terms of herd immunity, while having a death toll that is very similar to nations that destroyed their economy and sacrificed the population's mental health in the name of infection control.
Anders Tegnell, the chief epidemiologist in charge of Sweden's coronavirus response, has stated32 he does not believe Sweden will see a second wave with widespread contagion as the country is seeing a rapid decline in positive tests, indicating herd immunity has been achieved.33
He told The Guardian34 that the primary goal was always merely to slow the spread to avoid overwhelming medical services. The intention was never to prevent infection from spreading altogether, which has indeed proven impossible.
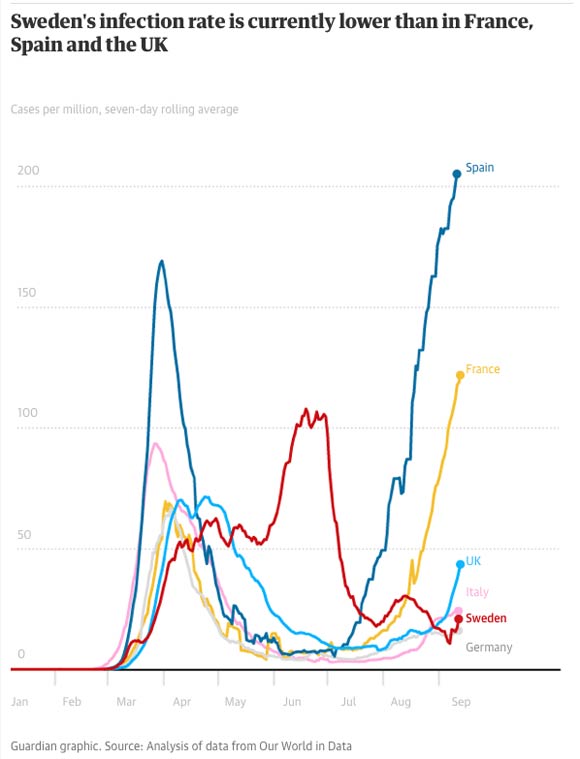
This was in fact the original plan just about everywhere. But while Sweden stuck to the original goal, and by mid-September boasted all-time low infection rates,35 other nations have twisted response plans to prevent infection transmission altogether, even among those for whom the risk of such an infection is vanishingly minor, such as school-aged children.
The two graphs from The Guardian,36 below, show Sweden's infection rate and deaths per million, compared to other countries that enforced stricter lockdown rules.
Herd Immunity Threshold Likely Below 50%
As reported in "Herd Immunity 'Ahead of Schedule'" experts initially estimated that 70% of the population or more would need to be immune before herd immunity would be achieved. Now, more than a dozen scientists claim the herd immunity threshold is likely below 50%.
As stated earlier, if this is true — and as you can see by the studies reviewed, it appears a majority do have some level of immunity — then the need for a vaccine more or less vanishes.
Herd immunity is calculated using reproductive number, or R-naught (R0), which is the estimated number of new infections that may occur from one infected person.37 R0 of below 1 (with R1 meaning that one person who's infected is expected to infect one other person) indicates that cases are declining while R0 above 1 suggests cases are on the rise.
It's far from an exact science, however, as a person's susceptibility to infection varies depending on many factors, including their health, age and contacts within a community. The initial R0 calculations for COVID-19's herd immunity threshold were based on assumptions that everyone has the same susceptibility and would be mixing randomly with others in the community.
"That doesn't happen in real life," Dr. Saad Omer, director of the Yale Institute for Global Health, told The New York Times.38 "Herd immunity could vary from group to group, and subpopulation to subpopulation," or even zip code. When real-world scenarios are factored into the equation, the herd immunity threshold drops significantly, with some experts saying it could be as low as 10% to 20%.
Researchers from Oxford, Virginia Tech and the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine are among those that found39,40 when individual variations in susceptibility and exposure are taken into account, the herd immunity threshold dips below 10%.
Independent news source Off-Guardian also cited41 data from Stockholm County, Sweden, which shows a herd immunity threshold of 17%,42 as well as an essay by Brown University professor Dr. Andrew Bostom, who noted:43
"Lead investigator Dr. Gomes, from the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, and her colleagues concluded: "naturally acquired immunity to SARS-CoV-2 may place populations over the herd immunity threshold once as few as 10-20% of its individuals are immune."44
Separate HIT [herd immunity threshold] calculations of 9%,45 10-20%,46 17%,47 and 43%48,49 — each substantially below the dogmatically asserted value of ~70%50 — have been reported by investigators from Tel-Aviv University, Oxford University, University College of London, and Stockholm University, respectively."
Declaration Urges Implementation of Herd Immunity Approach
All in all, there are many reasons to suspect that continued lockdowns, social distancing and mask mandates are completely unnecessary and will not significantly alter the course of this pandemic illness, or the final death count.
As reported by British Sky News,51 October 7, 2020, many respected scientists are now calling for a herd immunity approach to the pandemic, meaning governments should allow people who are not at significant risk of serious COVID-19 illness to go back to normal life. According to the article:52
"The so-called Great Barrington declaration, signed by leading experts from the universities of Oxford, Nottingham, Edinburgh, Exeter, Cambridge, Sussex and York, suggests herd immunity as a way forward.
The declaration states: 'The most compassionate approach that balances the risks and benefits of reaching herd immunity, is to allow those who are at minimal risk of death to live their lives normally to build up immunity to coronavirus through natural infection, while better protecting those who are at highest risk. We call this focused protection."
The declaration points out that current lockdown policies are having "devastating effects on short and long-term public health" that will result in excess mortality in the future, primarily among younger people and the working class.
from Articles https://ift.tt/3j1loRP
via IFTTT