Vitamin D in the Prevention of COVID-19
As noted by retired nursing teacher John Campbell1 in the video above, vitamin D is "an important immunological molecule" that likely plays role in the COVID-19 pandemic.
In his video commentary, Campbell reviews a number of recent papers stressing the importance of vitamin D, starting with a press release2 from the French National Academy of Medicine, dated May 22, 2020.
The press release correctly points out that vitamin D is a prohormone, meaning it acts as an endocrine hormone. As such, it has wide-ranging influence on health. There are vitamin D receptors throughout your body, in every tissue and organ. Campbell reviews some of the basics of where and how vitamin D is synthesized in the body.
In summary, vitamin D is synthesized in the dermis of your skin in response to ultraviolet light from the sun. From there, it is transported to your liver and kidneys, where it is converted into an active hormone that is then circulated throughout your body. People with liver or kidney problems may have a reduced ability to synthesize vitamin D. As noted by the French National Academy of Medicine, vitamin D:3
- Modulates (meaning it can upregulate and downregulate as needed) the function of your immune system by stimulating dendritic cells (which detect the presence of antigens such as viruses or bacteria) and macrophages (responsible for triggering immune responses and destroying pathogens)
- Regulates and suppresses the cytokine inflammatory response.4 The ability to downregulate the inflammatory response is particularly important for COVID-19, as out of control inflammation (cytokine storm) is a primary cause of death
Vitamin D — An Excellent Adjunct to Any Therapy
The French medical authority points out there's "a significant correlation between low serum vitamin D levels and mortality from COVID-19" — which one would expect considering its modulating and regulatory influence on immune function — and that "by mitigating the inflammatory storm and its consequences," vitamin D "could be considered as an adjunct to any form of therapy."
They cite research showing the inverse correlation between vitamin D and COVID-19 infection and mortality (the lower your vitamin D the greater your risk of infection and death) in European countries has a confidence value of 95.4%, meaning there's only a 4.6% chance that this correlation is due to chance alone.
The press release ends by recommending the French population take supplemental vitamin D, as it is a "simple and inexpensive measure." The French authority also recommends "rapid serum vitamin D testing in people over 60 years of age with COVID-19."
As noted by Campbell, this is "a remarkably good idea." In those who are found to be deficient in vitamin D, the French National Academy of Medicine recommends an initial bolus dose of 50,000 IUs to 100,000 IUs.
And, while vitamin D testing is not stressed for those under the age of 60, they do recommend that anyone under the age of 60 who receives a positive COVID-19 test start taking 800 IUs to 1,000 IUs of vitamin D per day anyway.
Prospective Vitamin D for COVID-19 Studies Are Underway
The French recommendations are in stark contrast to the U.S., where Big Pharma-controlled health authorities and media are still trying to frighten people away from vitamin D supplementation. One reason for this could be because a healthier population is less likely to line up for inoculation with a fast-tracked vaccine.
It's worth noting that while the French National Academy of Medicine and Campbell state there are no randomized controlled trials looking at vitamin D supplementation and COVID-19, this is not true. There are many such trials currently underway. They just haven't been completed and published yet, but you can find them (and may be able to enroll in them) by searching ClinicalTrials.gov.5
In the UK, there's the Covidence UK Study,6 an effort to collect data about how vitamin D deficiency impacts your COVID-19 risk. If you live in the U.K., you can sign up for the Covidence UK study here. According to Adrian Martineau, a professor of respiratory infection and immunity at Queen Mary University of London, who is leading the Covidence study:7
"Vitamin D could almost be thought of as a designer drug for helping the body to handle viral respiratory infections. It boosts the ability of cells to kill and resist viruses and simultaneously dampens down harmful inflammation, which is one of the big problems with Covid."
British Health Care Workers Get Free Vitamin D
Aside from the French, Scotland and the U.K. are also starting to take vitamin D optimization more seriously. For example, the British Frontline Immune Support Team is providing U.K. National Health Service workers with free liposomal vitamin C, vitamin D and zinc packs to bolster and regulate their immune function.8 As noted by The Frontline Immune Support Team, vitamin D:9
"… plays a critical role in your immune defense system, both in reducing flu-like days of illness if your blood level is sufficient, and in helping your immune system respond when under viral attack. It speeds up recovery from pneumonia.
Two in five adults have a level of vitamin D below 25nmol/l, especially in late winter months such as February and March, that is likely to almost double their risk of flu. A vitamin D level above 100 nmol/l correlates with the lowest numbers of flu-like days. The moral of the story is to get your level up as quickly as possible."
The British NHS is also assessing the evidence to determine whether vitamin D should be prescribed to hospitalized COVID-19 patients and as a prevention to high-risk groups.10
Scottish Government Recommends Daily Vitamin D Supplement
As of June 3, 2020, Scottish government COVID-19 guidance includes taking a daily vitamin D supplement. As reported by the Scotland Herald:11
"Official Scottish Government guidance issued on June 3 states that everyone, including children, 'should consider taking a daily supplement containing 10 micrograms of vitamin D.'
However, it is 'specifically recommended' to all pregnant and breastfeeding women; infants and children under five years old; people from minority ethnic groups with dark skin such as those of African, African-Caribbean and South Asian origin, who require more sun exposure to make as much vitamin D; and people who are confined indoors."
Data Support Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19
Several studies have noted the inverse relationship between low vitamin D and a higher risk for COVID-19-positive test results,12 severity of infection13,14 and mortality.15 These studies are correlation studies and do not confirm causation, but studies that will be able to prove causation are currently underway.
Examples of these correlation studies include The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing (TILDA),16,17 which suggests vitamin D deficiency could have serious implications for COVID-19. The researchers recommend adults over 50 take a vitamin D supplement year-round if they don't get enough sun exposure to optimize their levels.
Another Irish paper,18 "Vitamin D and Inflammation: Potential Implications for Severity of COVID-19," concluded there is "a strong plausible biological hypothesis and evolving epidemiological data supporting a role for vitamin D in COVID-19."
Some of those biological mechanisms have already been summarized above. Other mechanisms of action that can impact your risk of COVID-19 include the following:
|
SARS-CoV-2 is an enveloped virus, which means it's more difficult for your immune system to identify and destroy it. However, higher vitamin D levels are inversely associated with infection by many other enveloped viruses, including dengue, hepatitis, herpes, HIV, rotavirus, respiratory syncytial virus and influenza.19,20 We'll have to wait and see if the same holds true for SARS-CoV-2, but chances are it will. |
|
Vitamin D strengthens cellular junctions, thereby making it more difficult for viruses to gain entry through your eyes, ears, lungs and mucus membranes. This in turn makes the infection less likely to migrate down into your lungs.21 |
|
Vitamin D can reduce the risk of infection by lowering the rate at which the virus replicates and can reduce the pro-inflammatory cytokines that damage the lungs, leading to pneumonia. It also helps increase concentrations of anti-inflammatory cytokines that may help protect the lungs. For these reasons, researchers suggest people who are at risk for COVID-19 should take:22
|
|
Vitamin D is an important component in the prevention and treatment of influenza23 and upper respiratory tract infections.24 While vitamin D does not appear to have a direct effect on the virus itself, it strengthens immune function, thus allowing the host body to combat the virus more effectively.25 As detailed in "Vitamin D Prevents Infections," research shows high-dose vitamin D supplementation lowers the risk of respiratory illnesses and lung infections in the elderly by 40%. As noted by an author of that study, "Vitamin D can improve the immune system's ability to fight infections because it bolsters the first line of defense of the immune system." As mentioned earlier, vitamin D also suppresses inflammatory processes and inhibits excessive production of proinflammatory cytokines that give rise to a cytokine storm.26 Taken together, this might make vitamin D quite useful against COVID-19, because while robust immune function is required for your body to combat the virus, an overactivated immune system is also responsible for the cytokine storm we see in COVID-19 infection that can lead to death. |
|
Vitamin D upregulates production of human cathelicidin, LL-37, which has antimicrobial and antiendotoxin activities.27 |
|
Vitamin D supplementation has been shown to protect against acute respiratory infections.28 Daily or weekly supplementation (opposed to infrequent bolus doses) of vitamin D had the greatest protective effect in those with the lowest vitamin D levels.29 In one study,30 those with severe vitamin D deficiency who took a daily or weekly supplement cut their respiratory infection risk in half, whereas the acute administration of high bolus doses of vitamin D had no significant impact on infection risk. |
|
Data analysis31 by GrassrootsHealth shows people with a vitamin D level of at least 40 ng/mL reduced their risk of colds by 15% and flu by 41%, compared to those with a level below 20 ng/mL. |
COVID-19-Specific Papers
In addition to the Irish papers cited above, several others have come to the same or similar conclusions. Additional examples include:
|
The vitamin D review paper32 "Evidence That Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Death," published in the journal Nutrients, April 2, 2020, which states that:
|
|
A GrassrootsHealth review33 of an observational study involving 212 COVID-19 patients in Southeast Asia identified a correlation between vitamin D levels and disease severity. Those with the mildest disease had the highest vitamin D levels, and vice versa. In the initial study group of 212 patients (see Table 1 below), 55 had normal vitamin D levels, which was defined as greater than 30 ng/ml; 80 had insufficient levels of 21 to 29 ng/ml and 77 had deficient levels of less than 20 ng/ml. According to the research done by GrassrootsHealth, 40 ng/mL is the lower edge of optimal, with 60 ng/mL to 80 ng/mL being ideal for health and disease prevention. Despite that, the benefit of having a vitamin D level above 30 ng/mL was clear. 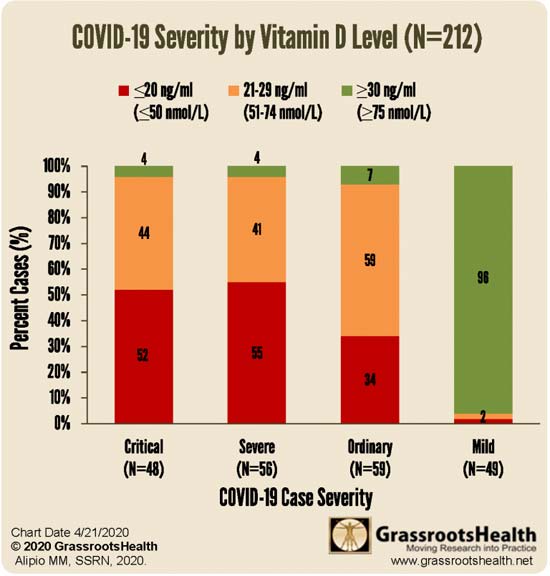 |
|
In a study34 that looked at data from 780 COVID-19 patients in Indonesia, those with a vitamin D level between 20 ng/mL and 30 ng/mL had a sevenfold higher risk of death than those with a level above 30 ng/mL. Having a level below 20 ng/mL was associated with a 12 times higher risk of death. |
|
Research35,36 posted on the preprint server MedRxiv June 10, 2020, reports a combination of vitamin D3, B12 and magnesium inhibited the progression of COVID-19 in patients over the age of 50, resulting in "a significant reduction in proportion of patients with clinical deterioration requiring oxygen support and/or intensive care support." |
|
"The Role of Vitamin D in the Prevention of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Mortality"37 — which looked at the average vitamin D levels and the number of COVID-19 cases and death rates in 20 European countries — found lower vitamin D levels correlated with higher caseloads and mortality. The authors concluded, "We believe that we can advise vitamin D supplementation to protect against SARS-CoV2 infection." |
|
Northwestern University researchers report finding an inverse relationship between vitamin D and CRP, a marker for inflammation. Those with higher CRP had lower vitamin D and vice versa. According to the authors:38
|
|
"The Possible Role of Vitamin D in Suppressing Cytokine Storm and Associated Mortality in COVID-19 Patients,"39,40 posted on the preprint portal medRxiv May 18, 2020, reports finding a strong correlation between severe vitamin D deficiency and higher mortality rates in countries across the globe. The researchers attribute this to a connection between low vitamin D and high risk for cytokine storms. The analysis suggests higher vitamin D levels among the general population could cut mortality in half by reducing complications.41 |
Now Is the Time to Optimize Your Vitamin D
Health experts are warning we're likely to see a second wave of COVID-19 this fall, as temperatures drop. This means the time to start optimizing your vitamin D is now.
Data from GrassrootsHealth's D*Action studies suggest the optimal level for health and disease prevention is between 60 ng/mL and 80 ng/mL, while the cutoff for sufficiency appears to be around 40 ng/mL. In Europe, the measurements you're looking for are 150 to 200 nmol/L and 100 nmol/L respectively.
I recently published a comprehensive vitamin D report in which I detail vitamin D's mechanisms of action and how to ensure optimal levels. I recommend downloading and sharing that report with everyone you know.

>>>>> Click Here <<<<<
A quick summary of the key steps is as follows:
1. First, measure your vitamin D level — One of the easiest and most cost-effective ways of measuring your vitamin D level is to participate in the GrassrootsHealth's personalized nutrition project, which includes a vitamin D testing kit.
Once you know what your blood level is, you can assess the dose needed to maintain or improve your level. If you cannot get enough vitamin D from the sun (you can use the DMinder app42 to see how much vitamin D your body can make depending on your location and other individual factors), then you'll need an oral supplement.
As previously detailed in "Magnesium and K2 Optimize Your Vitamin D Supplementation," it's strongly recommended to take magnesium and K2 concomitant with oral vitamin D. Data from nearly 3,000 individuals reveal you need 244% more oral vitamin D if you're not also taking magnesium and vitamin K2!43
What this means in practical terms is that if you take all three supplements in combination, you need far less oral vitamin D in order to achieve a healthy vitamin D level.
2. Assess your individualized vitamin D dosage — To do that, you can either use the chart below, or use GrassrootsHealth's Vitamin D*calculator. To convert ng/mL into the European measurement (nmol/L), simply multiply the ng/mL measurement by 2.5. To calculate how much vitamin D you may be getting from regular sun exposure in addition to your supplemental intake, use the DMinder app.44
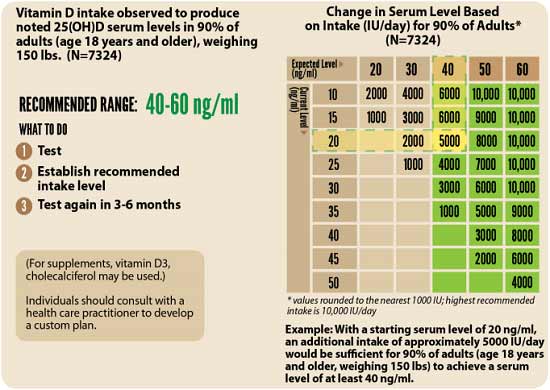
3. Retest in three to six months — Lastly, you'll need to remeasure your vitamin D level in three to six months, to evaluate how your sun exposure and/or supplement dose is working for you.
The Importance of Testing Your Vitamin D Levels
A growing body of evidence shows that vitamin D plays a crucial role in disease prevention and maintaining optimal health. There are about 30,000 genes in your body, and vitamin D affects nearly 3,000 of them, as well as vitamin D receptors located throughout your body.
For a more detailed and comprehensive analysis of the connection of vitamin D and COVID-19, please review the report I created that could be used to address any health care professionals who would disagree with this recommendation. Also included is a shortened version of the document which will be better to educate those that you would like to convince of the importance of getting your vitamin D levels optimized.

>>>>> Click Here <<<<<
Vitamin D Helps Protect Against Cancer and Other Diseases
According to one large-scale study, having optimal vitamin D levels can slash your risk of cancer and can help prevent at least 16 different types of cancer, including pancreatic, lung, ovarian, prostate and skin cancers.
Vitamin D from sun exposure also radically decreases your risk of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS) and Type 1 diabetes. Sun exposure also helps prevent osteoporosis, which is a significant concern for women in particular.
Magnesium Is Necessary to Activate Vitamin D
Since over half the population does not get enough magnesium and far more are likely deficient, magnesium supplementation is recommended when taking vitamin D supplements. This is because magnesium helps to activate vitamin D, as the enzymes that metabolize vitamin D in your liver and kidneys require magnesium.
What GrassrootsHealth observed in testing and analyzing nutrient intakes from over 15,000 patients is that about half of those taking vitamin D supplements were unable to normalize their vitamin D levels until they started to take supplemental magnesium.
They also found that those who do not take supplemental magnesium need, on average, 146% more vitamin D per day to achieve a healthy blood level of 40 ng/ml (100 nmol/L), compared to those who take at least 400 mg of magnesium along with their vitamin D supplement.
Omega-3 Fats Are Crucial to Your Well-Being
Meanwhile, recent research suggests high doses (4 grams) of the omega-3 fats EPA and DHA may help improve healing after a heart attack. Other benefits of omega-3 fats include prevention of lupus and Parkinson’s disease, decreased anxiety, healthier and stronger bones, as well as fighting fats in the body.
However, you can’t tell by looking in a mirror if you are deficient in vitamin D, magnesium or omega-3s. The only real way to know if you are deficient in these nutrients is to get tested.
How Much Vitamin D Should You Take
If you know your vitamin D level you can use the calculator below to find the best dose to take.
If you are unable or unwilling to get a vitamin D test, they have found that the average dose to achieve a healthy vitamin D level of 40 ng/ml is about 8,000 units per day. If you are underweight you will want to reduce this dose to 6-7,000 units per day as heavier people tend to need more vitamin D.
How to Test Your Levels
I'm really pleased GrassrootsHealth Nutrient Research Institute has expanded its research projects to include a range of different tests, seeing how deficiency may be needlessly affecting the health of so many. Like its Vitamin D*action Project, the Magnesium*PLUS Focus Project will allow us all to take action on known science with a consensus of experts without waiting for institutional lethargy.
The Vitamin D*action Project has truly demonstrated the value measurement can have on public health, and there’s no doubt in my mind that the Magnesium*PLUS Focus Project will have the same impact. As in earlier projects, once the study of a community is completed, all that information can be used to push for public health recommendations that will benefit everyone.

>>>>> Click Here <<<<<
You have the ability to participate in a variety of different tests, including:
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin D and Omega 3
- Vitamin D, Omega 3 and Magnesium
- Vitamin D, Magnesium & Omega 3 PLUS Elements. Remember, by participating in this public research project, you not only are identifying your own levels, but allowing yourself to make decisions about your diet and supplements to improve your health.
Your data (which is anonymous) will also help GrassrootsHealth researchers to determine the ideal levels for the prevention of various diseases, and what kind of dose-response relationship exists among the general population.
With the data from this project, individuals will be able to see what works for them, and, researchers will be able to demonstrate just to what extent health care costs may be reduced simply by getting people into an optimal range.
from Articles https://ift.tt/3ivsyig
via IFTTT