How Dietary Intervention Lifts Depression
This article was previously published October 24, 2019, and has been updated with new information.
Foods have an immense impact on your body and your brain, and eating whole foods as described in my nutrition plan is a good way to simultaneously support your mental and physical health. Avoiding sugar and artificial sweeteners is in my view, based on the evidence, a crucial aspect of preventing and/or treating depression.
Both contribute to chronic inflammation and can wreak havoc with your brain function. Recent research also shows how swapping processed junk food for a healthier diet can significantly improve depression symptoms, which really shouldn't come as a great surprise.
The Sugar Trap
Research1 published in 2014 linked sweetened beverages — both sugar- and artificially-sweetened — with an increased risk of depression. Those who drank more than four cans or glasses of soda a day had a 30% higher risk of depression compared to those who did not consume sweetened beverages of any kind.
Interestingly, fruit juices were even more hazardous. The same amount of sweetened fruit drinks (four glasses) was associated with a 38% higher risk of depression.
Overall, artificially sweetened so-called "diet" drinks were associated with the highest risks of depression, compared to beverages sweetened with sugar or high-fructose corn syrup. More specifically, compared to those who did not drink sweetened beverages:
- Those who drank primarily diet soda were 31% more likely to suffer with depression, whereas regular soda was associated with a 22% increased risk
- Those who drank primarily diet fruit drinks had a 51% higher risk for depression, while consuming regular fruit drinks was associated with a more modest 8% increased risk
- Drinking primarily diet iced tea was associated with a 25% increased risk for depression, whereas those who drank regular sweetened iced tea actually had a 6% reduced risk
Similarly, other research2 found adolescents who had elevated levels of sodium and low levels of potassium in their urine — two factors indicative of a diet high in junk food and processed food — had more frequent symptoms of depression.
According to the authors,3 "Given the substantial brain development that occurs during adolescence, individuals in this developmental period may be particularly vulnerable to the effects of diet on the neural mechanisms underlying emotion regulation and depression."
Why Sugar Takes a Toll on Mental Health
There are at least four potential mechanisms through which refined sugar intake could exert a toxic effect on mental health:
- Sugar (particularly fructose) and grains contribute to insulin and leptin resistance and impaired signaling, which play a significant role in your mental health
- Sugar suppresses activity of a key growth hormone called brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which promotes healthy brain neurons. BDNF levels are critically low in both depression and schizophrenia, which animal models suggest might actually be causative
- Sugar consumption also triggers a cascade of chemical reactions in your body that promote chronic inflammation. In the long term, inflammation disrupts the normal functioning of your immune system, which is linked to a greater risk of depression4
- Sugar impairs the microbiome and its influence on the modulation of stress response, immune function, neurotransmission and neurogenesis
In 2004, British psychiatric researcher Malcolm Peet published a provocative cross-cultural analysis5 of the relationship between diet and mental illness. His primary finding was a strong link between high sugar consumption and the risk of both depression and schizophrenia. According to Peet:
"A higher national dietary intake of refined sugar and dairy products predicted a worse 2-year outcome of schizophrenia. A high national prevalence of depression was predicted by a low dietary intake of fish and seafood.
The dietary predictors of ... prevalence of depression are similar to those that predict illnesses such as coronary heart disease and diabetes, which are more common in people with mental health problems and in which nutritional approaches are widely recommended."
One of the key predictors of heart disease and diabetes is in fact chronic inflammation which, as Peet mentions, is also associated with poor mental health. Sugar is a primary driver of chronic inflammation in your body, so consuming excessive amounts of sugar can truly set off an avalanche of negative health events — both mental and physical.
Three-Week Dietary Intervention Lifts Depression
More recently, a study6,7,8 published in the October 2019 issue of PLOS ONE said to be the first of its kind, found dietary intervention can effectively treat depression in young adults. The researchers enrolled 101 individuals aged 17 to 35, whose stress and depression scores indicated moderate to high levels of depression.
Participants were divided into two groups. One received dietary intervention while the other (controls) received no intervention. Dietary instructions were provided to the treatment group by a registered dietician via a 13-minute video, which could be revisited at will.
The dietary recommendations were based on the 2003 Australian Guide to Healthy Eating protocol "with additional recommendations to increase concordance with Mediterranean-style diets … and diet components (e.g., omega-3 fatty acids, cinnamon, turmeric) that have beneficial effects on neurological function."9 More specifically, the treatment group was instructed to eat:
|
Five servings of vegetables per day |
|
Two to three servings of fruit per day |
|
Three servings of wholegrain cereal per day |
|
Three servings of protein (such as lean meat, poultry, eggs or legumes) per day |
|
Three servings of unsweetened dairy per day |
|
Three servings of fish per week |
|
3 tablespoons of nuts and seeds per day |
|
2 tablespoons of olive oil per day |
|
1 teaspoon of turmeric and cinnamon on most days |
Refined carbohydrates, sugar, processed meats and soft drinks were to be avoided as much as possible. According to the authors:10
"There is strong epidemiological evidence that poor diet is associated with depression. The reverse has also been shown, namely that eating a healthy diet rich in fruit, vegetables, fish and lean meat, is associated with reduced risk of depression …
There was good compliance with the diet intervention recommendations assessed using self-report and spectrophotometry. The Diet group had significantly lower self-reported depression symptoms than the Control Group …
Reduced DASS-21 depression subscale scores were maintained on follow up phone call 3 months later. These results are the first to show that young adults with elevated depression symptoms can engage in and adhere to a diet intervention, and that this can reduce symptoms of depression."
Dietary Intervention Significantly Lowers Depression Scores
The first graph below illustrates the difference in primary depression scores (based on Centre for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale or CESD-R) between the two groups. The second graph illustrates the difference between the two groups based on DASS-21 depression subscale scores.
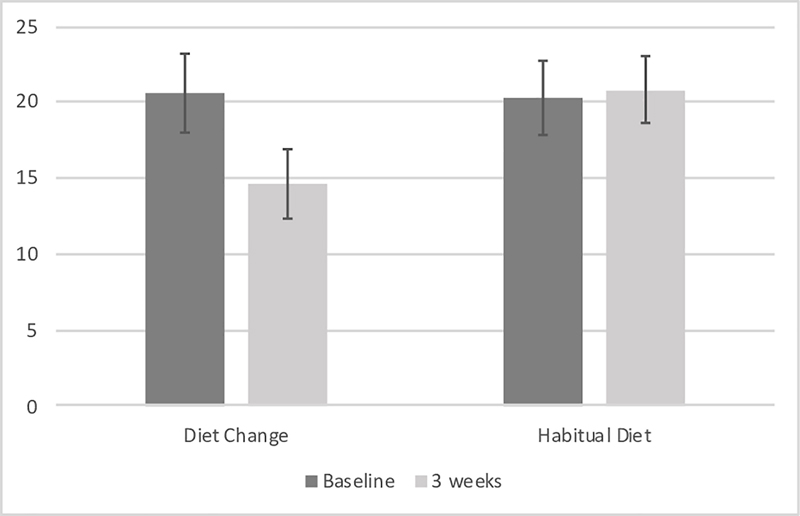
Source: PLOS ONE October 9, 2019, Figure 211
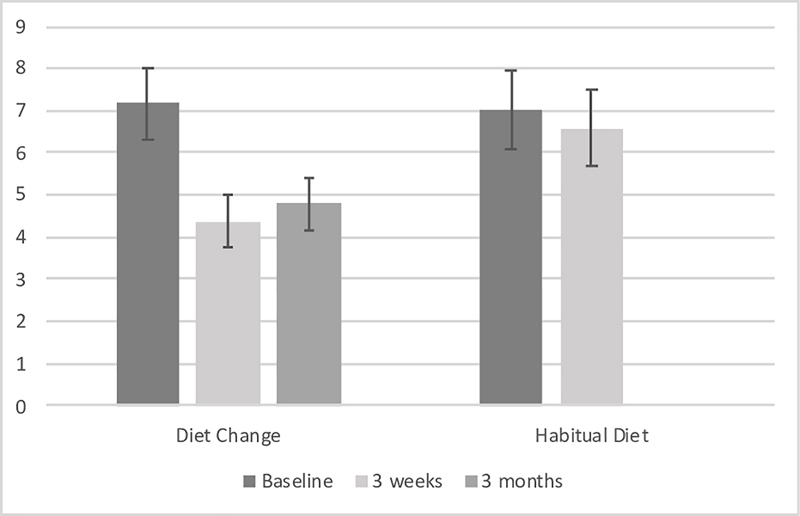
Source: PLOS One October 9, 2019, Figure 312
The researchers also report that the dietary intervention resulted in lower levels of anger. In the Discussion section of the paper, the authors make the following observations:13
"The results of this RCT provide support for improving diet as a useful adjunct treatment to reduce depressive symptoms … One of the most interesting findings is the fact that diet change was feasible in this population.
As the participants were young adults and university undergraduate students, we anticipated several potential barriers such as the perceived cost of the diet, the time demands of preparing food and/or reliance on others for food preparation (particularly if they lived at home).
Additionally, the participants were recruited based on self-reported symptoms of depression. We anticipated that the symptoms of depression, including low energy, reduced motivation and apathy, would present as barriers to eating well.
Despite these factors, there was a significant increase in the recommended foods and decrease in processed foods for the diet change group but not the habitual diet group.
Furthermore, within the diet change group, increase in recommended foods was associated with spectrophotometer readings. This provides objective evidence to support the participants' self-reported compliance with the diet …
Even in the general population, adherence to diet advice is typically very poor, with over 80% of Australians reporting that they do not comply with dietary recommendations.
As a result, there is substantial nihilism regarding the ability to change people's diets. The current study simply provided a brief 13-minute video, paper resources and minimal phone support.
The fact that this relatively low-cost intervention can result in a population of young adults adhering to diet recommendations is very promising. Furthermore, it is important to consider that participants in the current study did not need to adhere strictly to the diet recommendations to derive benefit."
Other Studies Support Dietary Intervention for Mental Health
Another recent paper found similar results. The meta-analysis,14 published in the April 2019 issue of Psychosomatic Medicine, looked at 16 randomized controlled trials with outcome data — based on a variety of depression scores — for 45,826 participants ranging in age from 21 to 85. Interventions ranged from 10 days to three years.
While all but one examined nonclinical depression, dietary interventions were still found to significantly reduce symptoms of depression. Interestingly, women appeared to reap the greatest benefits, not only for depression but also anxiety. According to the authors, "Dietary interventions hold promise as a novel intervention for reducing symptoms of depression across the population."
Interestingly, studies specifying the involvement of a nutritional professional had significantly better results than those in which the dietary advice was delivered without a professional's involvement.
However, as shown in the featured PLOS ONE study, this doesn't necessarily have to be a complicated affair. There, participants simply viewed a video in which a dietician gave the instructions.
Mechanisms of Action
In the Implications and Recommendations section of the Psychosomatic Medicine meta-analysis, the authors point out a number of possible mechanisms of action allowing depressed patients to benefit from nutritional intervention:15
"… diet may act via several pathways that are implicated in mental health. These include pathways related to oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction, which are disrupted in people with mental disorders.
Gut microbiota dysbiosis has also been implicated because of emerging research demonstrating involvement of the microbiome in the modulation of stress response, immune function, neurotransmission, and neurogenesis. A healthy diet typically contains a wide variety of bioactive compounds that can beneficially interact with these pathways.
For example, vegetables and fruits contain, in addition to beneficial vitamins, minerals and fiber, a high concentration of various polyphenols that seem to be associated with reduced rates of depression … potentially because of their anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and prebiotic properties.
Furthermore, vitamins (e.g., B vitamins), fatty acids (e.g., omega 3 fatty acids), minerals (e.g., zinc, magnesium), and fiber (e.g., resistant starch) as well as other bioactive components (e.g., probiotics), which are typically abundant in healthy dietary patterns, may also be protective from mental illness.
Along with increasing the intake of beneficial nutrients, dietary interventions may also impact on mental well-being by reducing the consumption of unhealthy food associated with increased risk for depression, such as processed meats, refined carbohydrates, and other inflammatory foods.
Unhealthy diets are also high in other compounds that may negatively affect these pathways. For example, elements commonly found in processed foods such as saturated fatty acids, artificial sweeteners, and emulsifiers may alter the gut microbiome, which may activate inflammatory pathways."
Nutritional Advice for Mental Health
Keeping inflammation in check is an important part of any effective mental health treatment plan. If you're gluten sensitive, you will need to remove all gluten from your diet. A food sensitivity test can help ascertain this. Reducing lectins may also be a good idea.
As a general guideline, eating a whole food diet as described in my optimal nutrition plan can go a long way toward lowering your inflammation level. A cornerstone of a healthy diet is limiting sugar of all kinds, ideally to no more than 25 grams a day.
In one study,16 men consuming more than 67 grams of sugar per day were 23% more likely to develop anxiety or depression over the course of five years than those whose sugar consumption was less than 39.5 grams per day. Certain nutritional deficiencies are also notorious contributors to depression, especially:
• Marine-based omega-3 fats — Omega-3 fats have been shown to improve major depressive disorder,17 so make sure you're getting enough omega-3s in your diet, either from wild Alaskan salmon, sardines, herring, mackerel and anchovies, or a high-quality supplement.
I recommend getting an omega-3 index test to make sure you're getting enough. Ideally, you want your omega-3 index to be 8% or higher.
• B vitamins (including B1, B2, B3, B6, B9 and B12) — Low dietary folate can raise your risk of depression by as much as 304%.18,19 A 2017 study20,21 showing the importance of vitamin deficiencies in depression involved suicidal teens. Most turned out to be deficient in cerebral folate and all of them showed improvement after treatment with folinic acid.
• Magnesium — Magnesium supplements have been shown to improve mild-to-moderate depression in adults, with beneficial effects occurring within two weeks of treatment.22
• Vitamin D — Studies have shown vitamin D deficiency can predispose you to depression and that depression can respond favorably to optimizing your vitamin D stores,23 ideally by getting sensible sun exposure.
A double-blind randomized trial24 published in 2008 concluded that supplementing with high doses of vitamin D "seems to ameliorate [depression] symptoms indicating a possible causal relationship." Research25 published in 2014 also linked low vitamin D levels with an increased risk for suicide.
The 2017 paper "Depression and Vitamin D Deficiency: Causality, Assessment and Clinical Practice Implications," published in the journal of Neuropsychiatry, notes:26
"The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, which enrolled a sample of 7,970 non-institutionalized U.S. residents age 15 to 39, confirmed that people with serum vitamin D ≤50 nmol/L [20 ng/mL] are at a significantly higher risk of showing depression than individuals whose serum levels of vitamin D are greater or equal to 75 nmol/L [30 ng/mL] …
A … large cohort study27 showed an association between low vitamin D levels and both presence and severity of depression, this suggesting the possibility that hypovitaminosis D indicates an underlying biological susceptibility for depression."
For optimal health, make sure your vitamin D level is between 60 and 80 ng/mL year-round. Ideally, get a vitamin D test at least twice a year to monitor your level.
Keeping your gut microbiome healthy also has a significant effect on your moods, emotions and brain.
Helpful Supplements
A number of herbs and supplements can also be used in lieu of drugs to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, including the following:
- St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) — This medicinal plant has a long historical use for depression, and is thought to work similarly to antidepressants, raising brain chemicals associated with mood such as serotonin, dopamine and noradrenaline.28
- S-Adenosyl methionine (SAMe) — SAMe is an amino acid derivative that occurs naturally in all cells. It plays a role in many biological reactions by transferring its methyl group to DNA, proteins, phospholipids and biogenic amines. Several scientific studies indicate that SAMe may be useful in the treatment of depression.
- 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) — 5-HTP is another natural alternative to traditional antidepressants. When your body sets about manufacturing serotonin, it first makes 5-HTP. Taking 5-HTP as a supplement may raise serotonin levels. Evidence suggests 5-HTP outperforms a placebo when it comes to alleviating depression,29 which is more than can be said about antidepressants.
- XingPiJieYu — This Chinese herb, available from doctors of traditional Chinese medicine, has been found to reduce the effects of "chronic, unpredictable stress," thereby lowering your risk of depression.30
Other Helpful Treatment Options
Evidence clearly shows antidepressants are not an ideal choice for most people with depression. Aside from diet, which I believe is foundational, the depression treatment with the most solid scientific backing is exercise. Other treatment suggestions include phototherapy, regular exercise, cognitive behavioral therapy, the Emotional Freedom Techniques and the importance of limiting your electromagnetic field exposure.
from Articles https://ift.tt/6MJZY8W
via IFTTT